0x00 WHUSESC 23-24 、 22-23 和 20-21 的数据结构实训期末考核题解源码
0x01 23-24 一、H 遍历算法设计 在森林上定义一种特殊的遍历次序,称为 H 遍历 。
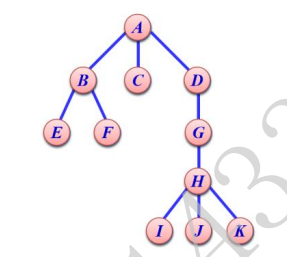
如图所示,该树的 H 遍历结果是:EBFACHIJKGD 。
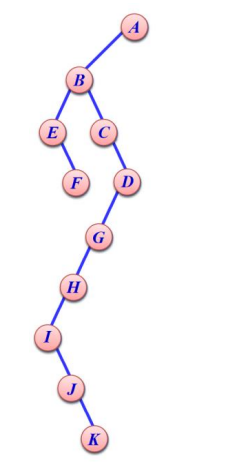
因为任意的树都可以转换为对应的二叉树,如上图所示的树,可以转换成下图所示的二叉树:
请设计一个算法,能够在以二叉链表 表示的树(即孩子兄弟链结构)上输出 H 遍历次序。
具体要求 (1) 定义二叉树的结点的数据类型,并使用动态内存分配 的方式向二叉树中插入新的结点。
(2) 定义栈元素的数据类型,以满足遍历二叉链表结构的需要。概念上是一个二叉树的结点入栈,同时应该表明该结点是其父结点的左孩子还是右孩子。这样可以方便判断回溯时是从左子树上来的还是从右子树上来的。
(3) 要求该算法是非递归算法 ,不允许使用递归。在算法中可以使用自定义的栈,也可以使用 C/C++ 库中的栈。
(4) 不允许将二叉链表结构改造成一般树的孩子链结构,也就是说,不允许在树上进行 H 遍历 ,而是要直接在对应的二叉树上进行 H 遍历。
(5) 算法执行完毕,要以正确的方式释放动态申请的空间 。
(6) 在遍历二叉树的过程中,遇到左子树为空,而右子树不空 的结点,要同时输出该结点及其父结点(如连续输出 E、B)。
(7) 在遍历二叉树的过程中,一旦对一个结点进行退栈操作 ,意味着要连续对一系列的结点进行退栈操作。条件包括右子树为空或者右子树已经处理完毕,或者左子树已经处理完毕且右子树为空。
(8) 当一个结点退栈,且是从非空的左子树回溯时,如果结点的子结点没有右孩子,应当输出该结点(如输出 G)。
(9) 在结点连续退栈的过程中,如果到达一个从左子树回溯的结点,且其右子树非空,则应输出其父结点的数据(如到达 B,输出 A)。
(10) 以本题所示的图中的树为数据,输出正确的 H 遍历的结果。
要求 main() 函数实现下述操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int main () { BTNode *root; makeTree(root); HTraverse(root); freeTree(root); return 0 ; }
实现 栈中额外记录一个状态,标志某个结点的第一个孩子是否访问,以此来遍历即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <unordered_map> #include <set> #include <unordered_set> #include <list> #include <climits> #include <utility> #include <string> using namespace std;class HBTree {private : struct BTNode { char data; BTNode* firstChild; BTNode* nextSiblings; BTNode (char val) : data (val), firstChild (nullptr ), nextSiblings (nullptr ) {} BTNode (char val, BTNode* p1, BTNode* p2) : data (val), firstChild (p1), nextSiblings (p2) {} }; struct stNode { BTNode* node; bool firstChildDone; stNode (BTNode* p, bool val) : node (p), firstChildDone (val) {} }; public : BTNode* root = nullptr ; BTNode* insert (char val, BTNode* parent) { if (parent == nullptr ) return nullptr ; BTNode* curNode = new BTNode (val); if (parent->firstChild == nullptr ) { parent->firstChild = curNode; }else { BTNode* tmpNode = parent->firstChild; while (tmpNode->nextSiblings != nullptr ) { tmpNode = tmpNode->nextSiblings; } tmpNode->nextSiblings = curNode; } return curNode; } void freeTree (BTNode* root) { if (root == nullptr ) return ; freeTree (root->firstChild); freeTree (root->nextSiblings); delete (root); } void makeTree (BTNode* &root) { BTNode* r = new BTNode ('K' , nullptr , nullptr ); r = new BTNode ('J' , nullptr , r); r = new BTNode ('I' , nullptr , r); r = new BTNode ('H' , r, nullptr ); r = new BTNode ('G' , r, nullptr ); r = new BTNode ('D' , r, nullptr ); r = new BTNode ('C' , nullptr , r); BTNode* l = new BTNode ('F' , nullptr , nullptr ); l = new BTNode ('E' , nullptr , l); r = new BTNode ('B' , l, r); r = new BTNode ('A' , r, nullptr ); root = r; } void HTravserse (BTNode* root) { stack<stNode> hst; hst.push ({root, false }); while (!hst.empty ()) { stNode& top = hst.top (); BTNode* curNode = top.node; if (!top.firstChildDone) { top.firstChildDone = true ; if (curNode->firstChild != NULL ) hst.push ({curNode->firstChild, false }); }else { cout << top.node->data << endl; hst.pop (); BTNode* sibling = curNode->firstChild; if (sibling != nullptr ) sibling = sibling->nextSiblings; else sibling = nullptr ; vector<BTNode*> siblings; while (sibling != nullptr ) { siblings.push_back (sibling); sibling = sibling->nextSiblings; } for (int i = siblings.size ()-1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { hst.push ({siblings[i], false }); } } } } }; int main () HBTree hbt; hbt.makeTree (hbt.root); hbt.HTravserse (hbt.root); hbt.freeTree (hbt.root); return 0 ; }
二、最大最小值差计算 对 n 个不同的正整数,进行如下操作:每一次删去其中两个数 a 和 b,然后加入一个新数:a*b+1,如此循环操作直到只剩下一个数。所有按这种操作方式最后得到的数中,最大的为 max ,最小的为 min ,计算 max - min 。
举例 假设有三个数 2, 4, 3 。
第一种循环操作 :取出 4, 3,将 4*3+1 放回序列,得到 2, 13;2*13+1 = 27。第二种循环操作 :取出 2, 3,将 2*3+1 放回序列,得到 4, 7;4*7+1 = 29。
所以,max - min = 29 - 27 = 2。
定理 每次从序列中取出两个最小的整数,循环操作可以得到 max。
定理已经给出,无需证明。
根据以上定理,编写一个算法得到一个正整数序列上的 max - min 的值。
具体要求 (1) 程序运行时,从键盘上输入序列长度 n,以及 n 个正整数值。
(2) 采用合适的数据结构,完成对 max 和 min 的计算。
(3) 所采用的数据结构,可以自己编写,也可以使用 C/C++ 中的库函数或者类。
(4) 输入多个不同的序列,都能够得到正确的结果。
(5) 使用 int 类型的变量,序列长度逐渐增加,程序运行会得到错误的结果,是何原因,如何解决?
(6) 在序列长度为 n 的情况下,分析算法复杂度。
实现 维护一个最大堆和一个最小堆即可;可以直接用优先队列,这里是手写的堆
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <unordered_map> #include <set> #include <unordered_set> #include <list> #include <climits> #include <utility> #include <string> using namespace std;class MinHeap { private : vector<long long > heap; public : bool empty () { return heap.empty (); } long long top () { return heap[0 ]; } void up (int idx) { while (idx > 0 ) { int p = (idx - 1 ) / 2 ; if (heap[p] > heap[idx]) { swap (heap[p], heap[idx]); idx = p; }else { break ; } } } void down (int idx) { int n = heap.size (); while (1 ) { int l = 2 * idx + 1 ; int r = 2 * idx + 2 ; int m = idx; if (l < n && heap[l] < heap[m]) { m = l; } if (r < n && heap[r] < heap[m]) { m = r; } if (m == idx) { break ; } swap (heap[m], heap[idx]); idx = m; } } void push (long long val) { heap.push_back (val); up (heap.size ()-1 ); } void pop () { swap (heap[0 ], heap.back ()); heap.pop_back (); down (0 ); } void make_heap () { int n = heap.size (); for (int i = n / 2 - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) down (i); } int size () { return heap.size (); } }; class MaxHeap { private : vector<long long > heap; public : bool empty () { return heap.empty (); } long long top () { return heap[0 ]; } void up (int idx) { while (idx > 0 ) { int p = (idx - 1 ) / 2 ; if (heap[p] < heap[idx]) { swap (heap[p], heap[idx]); idx = p; }else { break ; } } } void down (int idx) { int n = heap.size (); while (1 ) { int l = 2 * idx + 1 ; int r = 2 * idx + 2 ; int m = idx; if (l < n && heap[l] > heap[m]) { m = l; } if (r < n && heap[r] > heap[m]) { m = r; } if (m == idx) { break ; } swap (heap[m], heap[idx]); idx = m; } } void push (long long val) { heap.push_back (val); up (heap.size ()-1 ); } void pop () { swap (heap[0 ], heap.back ()); heap.pop_back (); down (0 ); } void make_heap () { int n = heap.size (); for (int i = n / 2 - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) down (i); } int size () { return heap.size (); } }; int main () MinHeap minh; MaxHeap maxh; int n; cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { long long val; cin >> val; minh.push (val); maxh.push (val); } while (minh.size () > 1 ) { long long val = minh.top (); minh.pop (); val = val * minh.top () + 1 ; minh.pop (); minh.push (val); } while (maxh.size () > 1 ) { long long val = maxh.top (); maxh.pop (); val = val * maxh.top () + 1 ; maxh.pop (); maxh.push (val); } long long min_val = minh.top (); long long max_val = maxh.top (); cout << max_val - min_val << endl; return 0 ; }
三、后缀表达式转中缀表达式 给定一个后缀表达式,如 ab+c*d+e*,将其转换成对应的中缀表达式,如 ((a+b)*c+d)*e。
为简化编程,所有的运算数量直接用单个字母表示,运算符只有 +、-、*、/ 四种。
具体要求 (1) 在中缀表达式中,考虑到运算符之间的优先级,在有需要使用括号 () 时,必须使用;
(2) 没有必要使用括号时,不允许出现多余的括号;
(3) 输入的后缀表达式是一个字符串,输出的中缀表达式也要求是一个字符串;
(4) 自行选用合适的辅助数据结构,如栈、队列等。这些辅助数据结构可以自行实现,也可以调用 C/C++ 函数库或者类库;
(5) 正确处理空间的申请和释放;
(6) 输入的后缀表达式有可能是非法的,要能识别表达式是否非法;
(7) 正确组织处理流程,输出的结果正确无误;
(8) 在不同的表达式上都取得正确的结果。
实现 用栈来模拟,遇到运算符就取出栈中两个单元;括号通过额外记录每个子表达式的主运算符来处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <unordered_map> #include <set> #include <unordered_set> #include <list> #include <climits> #include <utility> #include <string> using namespace std;class Expression {private : struct Exp { string expr; char op; Exp (): op (0 ) {} }; stack<Exp> st; public : Exp in; Exp post; bool is_op (char ch) { return (ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '*' || ch == '/' ); } bool is_let (char ch) { return (ch >= 0x61 && ch <= 0x7a ); } bool post2in () { for (int i = 0 ; i < post.expr.size (); i++) { if (!is_op (post.expr[i]) && !is_let (post.expr[i])) return false ; if (is_let (post.expr[i])) { Exp tmp; tmp.expr.push_back (post.expr[i]); st.push (tmp); }else { if (st.size () >= 2 ) { Exp& obj2 = st.top (); st.pop (); Exp& obj1 = st.top (); st.pop (); if (post.expr[i] == '*' || post.expr[i] == '/' ) { if (obj1. op == '+' || obj1. op == '-' ) { obj1. expr.insert (0 , "(" ); obj1. expr.push_back (')' ); } if (obj2. op == '+' || obj2. op == '-' ) { obj2. expr.insert (0 , "(" ); obj2. expr.push_back (')' ); } } obj1. expr.push_back (post.expr[i]); obj1. expr.append (obj2. expr); obj1. op = post.expr[i]; st.push (obj1); }else { return false ; } } } if (st.size () != 1 ) { return false ; }else { in = st.top (); return true ; } } }; int main () Expression e; cin >> e.post.expr; if (e.post2in ()) cout << e.in.expr << endl; else cout << "expression is invalid" << endl; return 0 ; }
0x02 22-23 一、定时队列问题 假设某一服务器要处理若干定时任务。这些任务按照时间的先后离开优先权队列(用最小堆 实现),出队列的任务被立即执行。
定时任务数据类型 1 2 3 4 5 struct TimedTask { long id; time_t t; };
t 是最小堆中排序的关键字(最小 t 的任务位于堆顶)。用户可在任务执行前撤销任务 或修改执行时间 。
为实现上述操作,另设一个散列表(哈希表) ,以 id 为关键字,每个元素是 {id, 在堆中的下标 idx} 的二元组。
具体要求 (1) 上推调整操作 bool adjustUp(TimedTask task_queue[], int pos, HashItem hash_table[], int hsize);true 代表上推过程中发生了数据交换。
(2) 下推调整操作 bool adjustDown(TimedTask task_queue[], int pos, int qsize, HashItem hash_table[], int hsize);true 代表下推过程中发生了数据交换。
(3) 散列表操作 插入、删除、修改 等操作(采用线性开地址法 )。adjustUp() 和 adjustDown() 函数都要考虑对散列表的同步操作。
(4) 按 id 删除堆中任意任务 void deleteFromHeap(TimedTask task_queue[], int qsize, HashItem hash_table[], int hsize, long id);最小代价 迅速将剩余任务重新组织成最小堆,并完成散列表的相应修改。
(5) 按 id 修改堆中任意任务的时间 t void updateHeap(TimedTask task_queue[], int qsize, HashItem hash_table[], int hsize, long id, time_t t);
(6) 测试与输出 (1237585, 7875), (237585, 7855), (127585, 875), (17585, 975), (47585, 17875), (585, 75)优先权队列 以及散列表 的内容(假设散列表长度为 7)。
要求 main() 函数实现如下操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 int main () { initializeHashTable(hashtable, 7 ); buildQueue(taskqueue, 6 , hashtable, 7 ); dispQueue(taskqueue, 6 ); updateHeap(taskqueue, 6 , hashtable, 7 , 237585 , 700 ); dispQueue(taskqueue, 6 ); deleteFromHeap(taskqueue, 6 , hashtable, 7 , 17585 ); dispQueue(taskqueue, 5 ); return 0 ; }
要求补充实现所有可能需要用到的函数和数据结构。
实现 今年考纲要点没有哈希表,于是懒得再手写实现直接用unordered_map,剩下的通过手写最小堆稍微改造即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <unordered_map> #include <set> #include <unordered_set> #include <list> #include <climits> #include <utility> #include <string> using namespace std;class TimeTask {private : struct Task { long id; time_t t; }; unordered_map<long , int > hashtable; vector<Task> taskqueue; public : bool empty () { return taskqueue.empty (); } Task top () { return taskqueue[0 ]; } bool adjustUp (int idx) { bool flag = false ; while (idx > 0 ) { int p = (idx - 1 ) / 2 ; if (taskqueue[p].t > taskqueue[idx].t) { hashtable[taskqueue[p].id] = idx; hashtable[taskqueue[idx].id] = p; swap (taskqueue[p], taskqueue[idx]); flag = true ; idx = p; }else { break ; } } return flag; } bool adjustDown (int idx) { bool flag = false ; int n = taskqueue.size (); while (1 ) { int l = 2 * idx + 1 ; int r = 2 * idx + 2 ; int m = idx; if (l < n && taskqueue[l].t < taskqueue[m].t) { m = l; } if (r < n && taskqueue[r].t < taskqueue[m].t) { m = r; } if (m == idx) { break ; } hashtable[taskqueue[m].id] = idx; hashtable[taskqueue[idx].id] = m; swap (taskqueue[m], taskqueue[idx]); flag = true ; idx = m; } return flag; } void deleteFromHeap (long id) { int idx = hashtable[id]; hashtable[id] = taskqueue.size () - 1 ; hashtable[taskqueue[taskqueue.size ()-1 ].id] = idx; swap (taskqueue[idx], taskqueue.back ()); hashtable.erase (taskqueue.back ().id); taskqueue.pop_back (); if (!adjustDown (idx)) adjustUp (idx); } void updateHeap (long id, time_t t) { int idx = hashtable[id]; taskqueue[idx].t = t; if (!adjustDown (idx)) adjustUp (idx); } void push (Task obj) { taskqueue.push_back (obj); adjustUp (taskqueue.size ()-1 ); } void pop () { swap (taskqueue[0 ], taskqueue.back ()); taskqueue.pop_back (); adjustDown (0 ); } void make_heap () { int n = taskqueue.size (); for (int i = n / 2 - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) adjustDown (i); } void initializeHashTable () { hashtable[1237585 ] = 0 ; hashtable[237585 ] = 1 ; hashtable[127585 ] = 2 ; hashtable[17585 ] = 3 ; hashtable[47585 ] = 4 ; hashtable[585 ] = 5 ; } void buildQueue () { taskqueue.push_back ({1237585 , 7875 }); taskqueue.push_back ({237585 , 7855 }); taskqueue.push_back ({127585 , 875 }); taskqueue.push_back ({17585 , 975 }); taskqueue.push_back ({47585 , 17875 }); taskqueue.push_back ({585 , 75 }); make_heap (); } void dispQueue () { for (auto & task : taskqueue) { cout << task.id << " " << task.t << endl; } } }; int main () TimeTask tt; tt.initializeHashTable (); tt.buildQueue (); tt.dispQueue (); tt.updateHeap (237585 ,700 ); tt.dispQueue (); tt.deleteFromHeap (17585 ); tt.dispQueue (); return 0 ; }
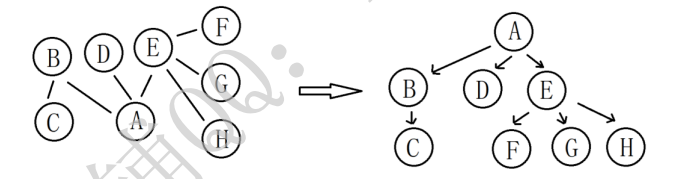
二、无向图的树判定与有根树转换 输入一个无向图的邻接矩阵,判断该无向图是否为一棵无根无向树 。若是,则设计算法将其转换成一棵具有最小高度的有根有向树 ,并输出其后序序列。
具体要求 (1) 输入表示
(2) 无根无向树判定算法
(3) 有根有向树转换 指定某顶点为树根 的情况下,将邻接矩阵转换成一棵用于无元链存储 的有根有向树。
(4) 后序遍历输出 后序遍历序列 。
(5) 最优树根寻找与最小高度树生成 最优树根 (使生成的有根有向树高度最小)。找到最优根后,生成最小高度的有根有向树 并输出其后序序列。
求所有顶点对之间的路径长度(参考 Floyd 算法 ),求出最大路径长度 。
根据该最大路径长度,深度优先遍历 到该路径上的所有顶点。
在该路径上选择最优根 。
实现 用并查集来判断无环且连通即是无根无向树;用 bfs 来建树;floyd 板子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <unordered_map> #include <set> #include <unordered_set> #include <list> #include <climits> #include <utility> #include <string> using namespace std;#define A 0 #define B 1 #define C 2 #define D 3 #define E 4 #define F 5 #define G 6 #define H 7 class Graph2Tree {public : vector<vector<int >> matrix; private : const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ; int n; struct Node { int data; Node* firstChild; Node* nextSibling; Node (int val) : data (val), firstChild (nullptr ), nextSibling (nullptr ) {} }; Node* root; vector<int > fa; int find (int x) { if (fa[x] != x) fa[x] = find (fa[x]); return fa[x]; } void Union (int x, int y) { fa[find (x)] = find (y); } void init (int n_) { n = n_; matrix.assign (n, vector <int >(n, INF)); fa.resize (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) fa[i] = i; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) matrix[i][i] = 0 ; root = nullptr ; } public : Graph2Tree (int n_ = 0 ) { init (n_); } void add (int u, int v, int w, bool undirected = true ) { matrix[u][v] = min (matrix[u][v], w); if (undirected) matrix[v][u] = min (matrix[v][u], w); } pair<vector<vector<int >>, vector<vector<int >>> floyd () { vector<vector<int >> dist; vector<vector<int >> path; dist = matrix; path.assign (n, vector <int >(n, -1 )); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) if (dist[i][j] < INF && i != j) path[i][j] = j; for (int k = 0 ; k < n; k++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (dist[i][k] < INF && dist[k][j] < INF && dist[i][j] > dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]) { dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]; path[i][j] = path[i][k]; } } } } return {dist, path}; } bool isTree () { for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (matrix[i][j] != INF && matrix[i][j] != 0 ) { if (find (i) == find (j)) return false ; else Union (i, j); } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int r = find (0 ); if (find (i) != r) return false ; } return true ; } Node* insert (Node* parent, int val) { if (parent == NULL ) return NULL ; Node* node = new Node (val); if (parent->firstChild == NULL ) { parent->firstChild = node; } else { Node* cur = parent->firstChild; while (cur->nextSibling != NULL ) { cur = cur->nextSibling; } cur->nextSibling = node; } return node; } bool matrix2tree (int rootval) { if (!isTree ()) return false ; clearTree (); root = new Node (rootval); vector<bool > vis (n, false ) ; queue<Node*> q; vis[rootval] = true ; q.push (root); while (!q.empty ()) { Node* cur = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (matrix[cur->data][i] != INF && matrix[cur->data][i] != 0 && !vis[i]) { q.push (insert (cur, i)); vis[i] = true ; } } } return true ; } void clearTree () { if (root == nullptr ) return ; stack<Node*> st; st.push (root); while (!st.empty ()) { Node* cur = st.top (); st.pop (); if (cur->firstChild != nullptr ) st.push (cur->firstChild); if (cur->nextSibling != nullptr ) st.push (cur->nextSibling); delete cur; } root = nullptr ; } void dfsTree () { if (root == nullptr ) return ; stack<pair<Node*, bool >> st; st.push ({root, false }); while (!st.empty ()) { Node* cur = st.top ().first; if (st.top ().second) { cout << char (cur->data+'A' ) << endl; st.pop (); }else { st.top ().second = true ; Node* tmp = cur->firstChild; vector<Node*> v; while (tmp != nullptr ) { v.push_back (tmp); tmp = tmp->nextSibling; } for (int i = v.size ()-1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { st.push ({v[i], false }); } } } } int getTreeHeight () { if (root == nullptr ) return -1 ; int h = 0 ; Node* cur = root; while (cur->firstChild != nullptr ) { cur = cur->firstChild; h++; } return h; } int getMinRootval () { auto tmp = floyd (); vector<vector<int >> dist = tmp.first; vector<vector<int >> next = tmp.second; int start, dest, maxp = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (dist[i][j] > maxp && dist[i][j] < INF) { maxp = dist[i][j]; start = i; dest = j; } } } vector<int > path; path.push_back (start); while (start != dest) { start = next[start][dest]; path.push_back (start); } int minHeight = INF; int minRootval = -1 ; for (auto & p : path) { matrix2tree (p); int height = getTreeHeight (); if (minHeight > height) { minHeight = height; minRootval = p; } } return minRootval; } void reset (int n_) { clearTree (); init (n_); } }; int main () Graph2Tree g (8 ) ; g.add (A, B, 1 ); g.add (B, C, 1 ); g.add (A, D, 1 ); g.add (A, E, 1 ); g.add (E, F, 1 ); g.add (E, G, 1 ); g.add (E, H, 1 ); g.matrix2tree (g.getMinRootval ()); g.dfsTree (); g.clearTree (); return 0 ; }
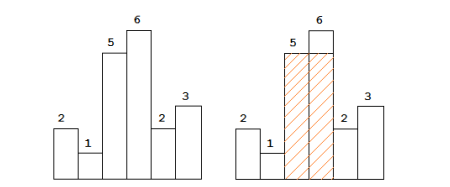
三、柱状图中最大矩形面积 给定 n 个非负整数,表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,宽度为 1。求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积 。
例如,图中阴影部分为可勾勒出的最大矩形,面积为 10。
具体要求 (1) 函数原型 int maxRectangle(int A[], int n)A 是存储柱状图高度的数组,n 为数组长度。
(2) 实现方式 非递归方式 实现该算法。
(3) 数组修改 允许改变数组 A 的内容。
(4) 递增情况分析 递增 时(递减情况类似)最容易求解,每根柱子都可向右扩展。因此,可先尝试在柱状图高度递增 的情况下求解。
(5) 通用解法(使用递增栈) 递增栈 (栈中元素按增序排列)作为辅助数据结构,解决任意形状 柱状图的最大矩形面积问题。
实现 单调栈板子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <unordered_map> #include <set> #include <unordered_set> #include <list> #include <climits> #include <utility> #include <string> using namespace std;class maxRect {public : vector<int > A; int maxRectangle () { int n = A.size (); stack<int > st; vector<int > mp (n) ; int res = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { while (!st.empty () && A[i] < A[st.top ()]) { mp[st.top ()] = i; st.pop (); } st.push (i); } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int cur = A[i] * (mp[i] - i); res = max (cur, res); } return res; } }; int main () maxRect s; s.A.push_back (2 ); s.A.push_back (1 ); s.A.push_back (5 ); s.A.push_back (6 ); s.A.push_back (2 ); s.A.push_back (3 ); cout << s.maxRectangle () << endl; }
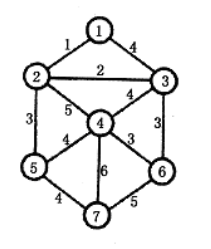
0x03 20-21 一、基于 Kruskal 算法的最小代价生成树 编写代码利用 Kruskal 算法 求解给定无向图的最小代价生成树。
具体要求 (1) 图的存储表示 邻接表 或邻接矩阵 的形式表示出来。
(2) 基于堆的边选取
初始化时,将所有边按权值大小建堆(heap) 。
每次取出堆顶元素后,立即调整使之恢复成堆。
建堆和后续堆顶操作都依赖 “筛选”(下推) 操作。
必须显式实现函数:void adjustDown(EdgeType edge_set[], int pos1, int pos2);
(3) 并查集设计与实现 数组中的双亲表示法 存储,并优化为以下结构(树高为 2):
每个结点包含数据域和两个指针域 (实际实现为整数下标)。
根结点 :第一指针指向自己(标识为根),第二指针指向任意一个孩子结点(若无孩子则为空)。孩子结点 :第一指针指向根结点,第二指针指向根结点的下一个孩子(形成单向循环链表)。两棵子树合并时,将规模较小的子树 合并进规模较大的子树,并保持上述结构。
必须显式实现合并(Union) 和查询(Find) 操作。
(4) 输出生成树及总代价 输出每一条边 ,并输出最小生成树的总代价 。
(5) 代码组织 不允许将所有代码都写在 main() 函数中 。合理组织头文件和源文件。
(6) 代码风格
实现 改造一下最小堆再加上kruskal即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <unordered_map> #include <set> #include <unordered_set> #include <list> #include <climits> #include <utility> #include <string> using namespace std;class MST {private : const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ; int n; vector<vector<pair<int , int >>> adj; struct EdgeHeap { struct Edge { int u, v, w; bool operator <(const Edge &e) const { return w < e.w; } }; vector<Edge> edges; void clear () { edges.clear (); } bool empty () { return edges.empty (); } Edge top () { return edges[0 ]; } void adjustUp (int idx) { while (idx > 0 ) { int p = (idx - 1 ) / 2 ; if (edges[idx] < edges[p]) { swap (edges[p], edges[idx]); idx = p; }else { break ; } } } void adjustDown (int idx) { int n = edges.size (); while (1 ) { int l = 2 * idx + 1 ; int r = 2 * idx + 2 ; int m = idx; if (l < n && edges[l] < edges[m]) { m = l; } if (r < n && edges[r] < edges[m]) { m = r; } if (m == idx) { break ; } swap (edges[m], edges[idx]); idx = m; } } void push (Edge e) { edges.push_back (e); adjustUp (edges.size ()-1 ); } void pop () { swap (edges[0 ], edges.back ()); edges.pop_back (); adjustDown (0 ); } void make_heap () { int n = edges.size (); for (int i = n / 2 - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) adjustDown (i); } }; EdgeHeap edges; vector<int > fa; int find (int x) { if (fa[x] != x) fa[x] = find (fa[x]); return fa[x]; } void Union (int x, int y) { fa[find (x)] = find (y); } void init (int n_) { n = n_; adj.assign (n, {}); edges.clear (); fa.resize (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) fa[i] = i; } public : MST (int n_ = 0 ) { init (n_); } void reset (int n_) { init (n_); } void add (int u, int v, int w, bool undirected = true ) { adj[u].push_back ({v, w}); if (undirected) adj[v].push_back ({u, w}); if (!undirected || u < v) edges.push ({u, v, w}); else if (undirected) edges.push ({v, u, w}); } int kruskal () { for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) fa[i] = i; int res = 0 ; int cnt = 0 ; while (!edges.empty ()) { auto e = edges.top (); edges.pop (); if (find (e.u) != find (e.v)) { Union (e.u, e.v); res += e.w; cnt++; cout << e.u+1 << "--" << e.v+1 << endl; if (cnt == n - 1 ) break ; } } cout << "total cost:" << res << endl; return (cnt < n - 1 ) ? -1 : res; } }; int main () MST g (7 ) ; g.add (0 , 1 , 1 ); g.add (0 , 2 , 4 ); g.add (1 , 2 , 2 ); g.add (1 , 3 , 5 ); g.add (2 , 3 , 4 ); g.add (1 , 4 , 3 ); g.add (2 , 5 , 3 ); g.add (3 , 4 , 4 ); g.add (3 , 5 , 3 ); g.add (3 , 6 , 6 ); g.add (4 , 6 , 4 ); g.add (5 , 6 , 5 ); g.kruskal (); return 0 ; }
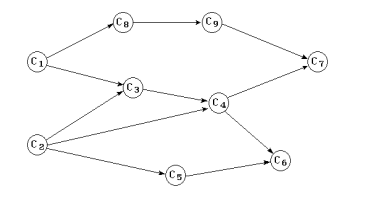
二、有向图拓扑序列计算 输入一个有向图,计算并输出该有向图的一个拓扑序列 。如果该有向图没有拓扑序列,则输出“没有拓扑序列”的提示。
具体要求 (1) 图的存储 邻接矩阵 表示,存放在数组 int graph[9][9] 中。
(2) 非递归 DFS 实现拓扑排序 深度优先遍历(DFS) 的思想构造拓扑序列,但算法不表现为递归函数 ,而是用自建的栈或队列 存放临时数据。
(3) 逆拓扑序列生成与反转 C_1 为出发顶点,进行单趟 DFS,每个顶点在退栈时输出 。若一次 DFS 后还有顶点未被访问,则重复以上操作,直到所有顶点都被访问并输出,得到一个逆拓扑序列 。将逆拓扑序列反向输出 即得到拓扑序列。
(4) 序列唯一性 唯一 的,若有错误将扣分。
(5) 回路检测 <C_0, C_2> 后,算法必须发现回路 并提示不能生成拓扑序列。
(6) 代码组织 不允许将所有代码都写在 main() 函数中 。合理组织头文件和源文件。
(7) DFS 函数原型 bool DFS(int idx, int path[], int &d);
idx:顶点编号。path:存放逆拓扑序列的数组。d:path 中下一个插入数据的下标。返回值:false 表示发现回路,不能生成拓扑序列。
要求数组 path 的空间在 DFS() 之外动态申请和释放 。
(8) 效率与风格
实现 使用栈模拟,栈元素增加一个状态标记
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <unordered_map> #include <set> #include <unordered_set> #include <list> #include <climits> #include <utility> #include <string> using namespace std;#define C1 0 #define C2 1 #define C3 2 #define C4 3 #define C5 4 #define C6 5 #define C7 6 #define C8 7 #define C9 8 class Topo {public : vector<vector<pair<int , int >>> adj; vector<vector<int >> matrix; private : const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ; int n; vector<int > fa; int find (int x) { if (fa[x] != x) fa[x] = find (fa[x]); return fa[x]; } void Union (int x, int y) { fa[find (x)] = find (y); } void init (int n_) { n = n_; adj.assign (n, {}); matrix.assign (n, vector <int >(n, INF)); fa.resize (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) fa[i] = i; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) matrix[i][i] = 0 ; } public : Topo (int n_ = 0 ) { init (n_); } void reset (int n_) { init (n_); } void add (int u, int v, int w, bool undirected = false ) { adj[u].push_back ({v, w}); if (undirected) adj[v].push_back ({u, w}); matrix[u][v] = min (matrix[u][v], w); if (undirected) matrix[v][u] = min (matrix[v][u], w); } vector<int > topological_sort_dfs () { vector<int > state (n, 0 ) ; stack<pair<int , bool >> st; vector<int > order; for (int i = n; i >= 0 ; i--) { if (state[i] != 0 ) continue ; st.push ({i, false }); while (!st.empty ()) { auto [u, finished] = st.top (); st.pop (); if (finished) { state[u] = 2 ; order.push_back (u); continue ; } if (state[u] == 1 ) { cout << "Graph has a cycle, topological sort not possible." << endl; return {}; } if (state[u] == 2 ) continue ; state[u] = 1 ; st.push ({u, true }); for (auto it = adj[u].rbegin (); it != adj[u].rend (); ++it) { int v = it->first; if (state[v] == 0 ) { st.push ({v, false }); } else if (state[v] == 1 ) { cout << "Graph has a cycle, topological sort not possible." << endl; return {}; } } } } reverse (order.begin (), order.end ()); return order; } }; int main () Topo g (9 ) ; g.add (C1, C3, 1 ); g.add (C1, C8, 1 ); g.add (C2, C3, 1 ); g.add (C2, C4, 1 ); g.add (C2, C5, 1 ); g.add (C8, C9, 1 ); g.add (C9, C7, 1 ); g.add (C4, C7, 1 ); g.add (C4, C6, 1 ); g.add (C5, C6, 1 ); g.add (C3, C4, 1 ); vector<int > o = g.topological_sort_dfs (); for (auto & e : o) { cout << 'C' << e+1 << endl; } g.add (C6, C2, 1 ); o.clear (); o = g.topological_sort_dfs (); return 0 ; }